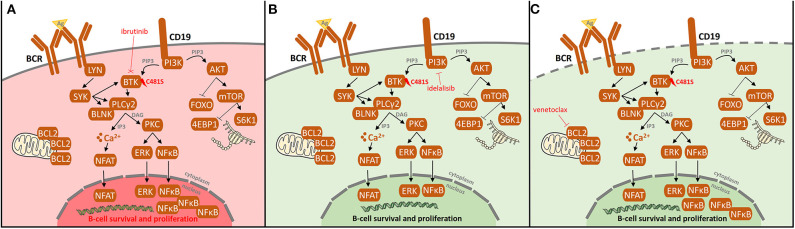
Figure 5.
Resistance-associated BTK (C481) mutation and possibilities of its overcoming in ibrutinib-treated CLL patients. (A) After the occurrence of BTK (C481) mutation, ibrutinib does not bind to BTK causing the loss of its therapeutic effect leading to BCR and NF-kB pathway activation, both signaling pathways pivotal for maintenance and proliferation of CLL cells. Additionally, activating mutations in PLCG2 gene may result in continuous BCR signaling independently on BTK activation. To overcome the resistance by mutations in BTK/PLCG2 genes, other pathways may be targeted. (B) Idelalisib targets phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), resulting in the downregulation of PI3K/mTOR signaling pathway, irrespectively on the BTK mutation status. (C) Venetoclax targets BCL-2, thus leading to the apoptosis of CLL cells. As the previous treatment with BCR inhibitors results in an increased dependence on BCL-2 expression together with the fact that venetoclax complements ibrutinib-mediated apoptosis, a deep therapeutic effect on venetoclax is achieved.