FIGURE 2.
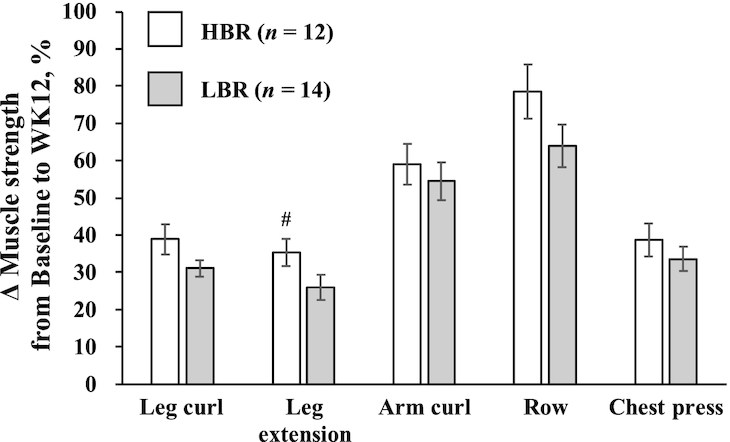
Comparison of percentage change in muscle strength from baseline to week 12 (WK12) in healthy young men with high (HBR) or low (LBR) relative protein intakes at breakfast. Values are indicated as means ± SEs, n = 12 (HBR) and n = 14 (LBR). Statistical analysis was performed with an independent t test to compare percentage change from baseline to week 12 in muscle strength between groups. #Tended to differ from LBR, P = 0.069. The HBR (“high breakfast”) group consumed a protein-enriched meal at breakfast to achieve a protein intake >0.24 g/kg body weight, reported as the required protein intake at all 3 meals to maximize muscle protein synthesis (23). The LBR (“low breakfast”) group consumed a provided meal at breakfast to achieve a protein intake >0.24 g/kg body weight at only 2 meals (lunch and dinner).
