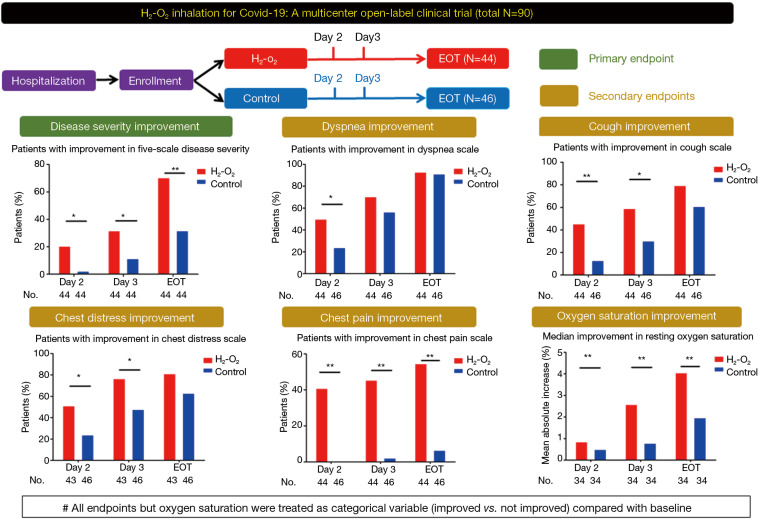
Figure 1.
Study design and the main treatment effects of H2-O2 inhalation in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 who had dyspnea at enrollment. All endpoints but resting oxygen saturation were treated as categorical variables (improved vs. not improved) compared with the baseline levels. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01. EOT, end-of-treatment, which was the day before hospital discharge.