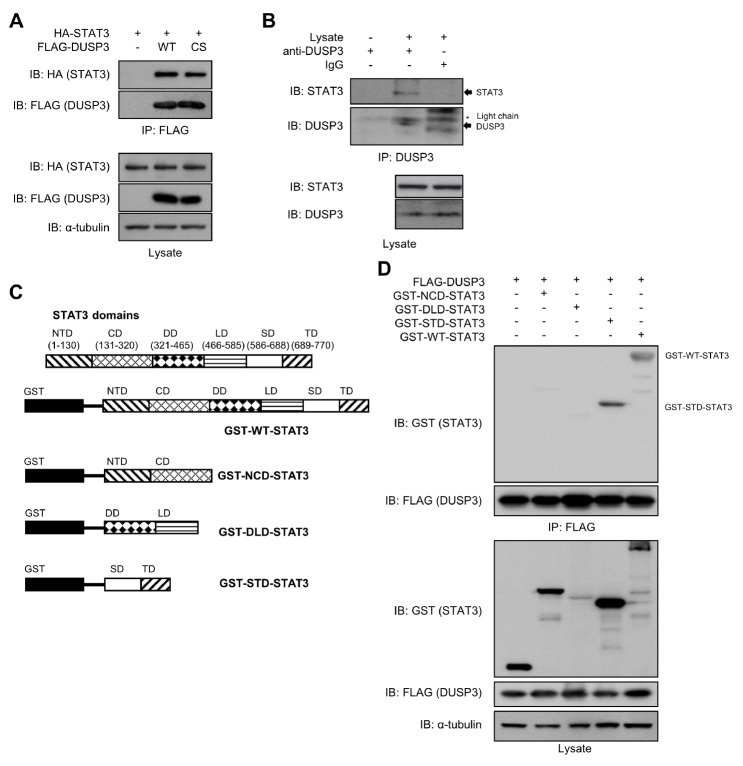
Fig. 2.
Interaction between DUSP3 and STAT3. (A) HEK 293 cells were co-transfected with FLAG-DUSP3 WT or CS and HA-STAT3. The interaction between FLAG-DUSP3 and STAT3 was analyzed by co-immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG conjugated beads, and the bound STAT3 was subjected to immunoblotting analysis using an anti-HA specific antibody. (B) Hep3B cells were stimulated with IL-6 (100 ng/mL) for 1 h. The interaction between DUSP3 and STAT3 was analyzed by co-immunoprecipitation with anti-DUSP3-specific antibody and protein agarose A/G beads, and the bound STAT3 was subjected to immunoblotting analysis using an anti-STAT3 specific antibody. (C) Human STAT3 consists of 6 domains: N-terminal domain, a coiled-coil domain, DNA-binding domain, linker domain, SH2 domain, and transactivation domain. The constructs of the STAT3 truncated forms were designed to include two domains in each construct. (D) HEK 293 cells were co-transfected with FLAG-DUSP3 and GST-tagged truncated or WT-STAT3. The interaction between DUSP3 and GST-STAT3 constructs was observed by co-immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting analysis. WT, wild type; CS, C124S; ND, N-terminal domain; CD, coiled-coil domain; DD, DNA-binding domain; LD, linker domain; SD, SH2 domain; TD, transactivation domain; NCD, N-terminal-coiled-coil domain; DLD, DNA-binding-linker domain; STD, SH2-transactivation domain.