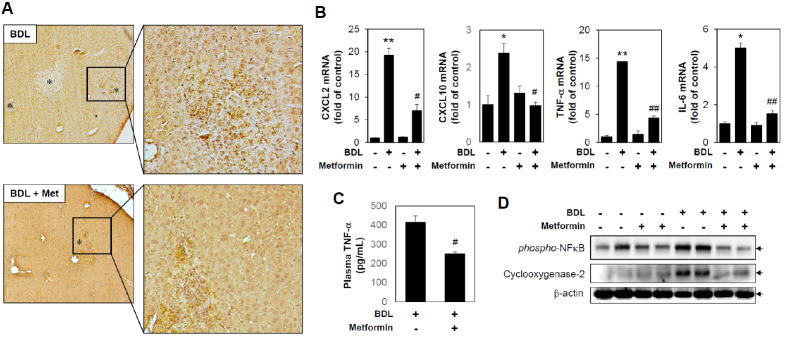
Fig. 2.
Metformin reduces bile duct ligation-induced neutrophil infiltration and inflammation. Sham or BDL-operated mice were injected with metformin (oral garbage, 200 mg/kg/day) for 3 days, and then liver tissues were harvested (n = 5). (A) Immunohistochemical staining of neutrophils in a liver tissue section (original magnification, ×100). * indicates necrotic area. (B) mRNA levels of CXCL2, CXCL10, TNF-α, and IL-6 were measured by performing qRT-PCR. Relative expression levels were normalized to GAPDH. Results are expressed as mean ± SD values and are representative of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. Sham, #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 vs. BDL. (C) Amounts of plasma TNF-α were determined by ELISA assay. Results are expressed as mean ± SE values and are representative of three independent experiments. #P < 0.05 vs. BDL. (D) Protein levels were measured by immunoblotting with antibodies against phospho- NFkB, Cyclooxygenase-2 and b-actin. BDL: bile duct ligation, Met: metformin.