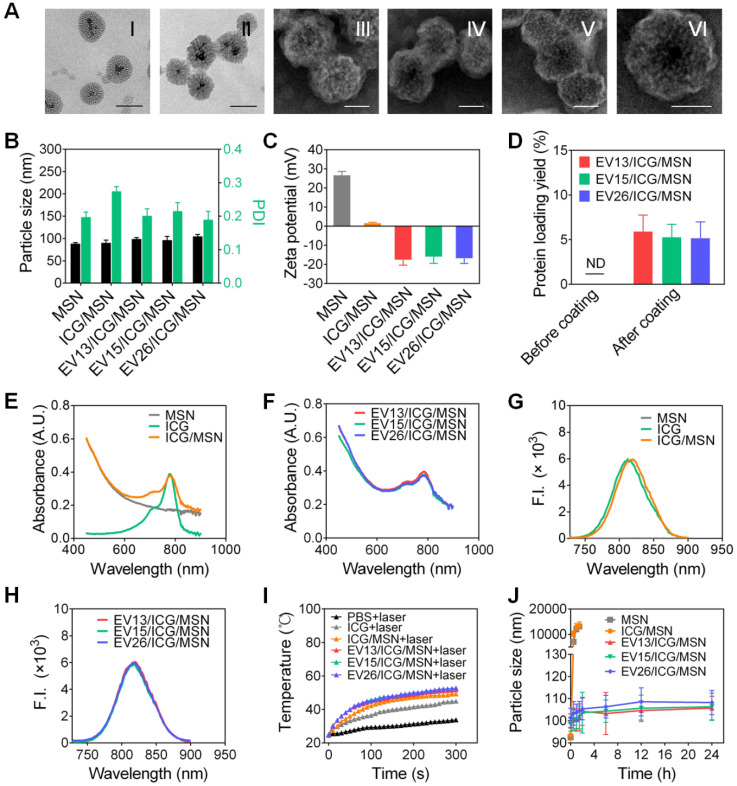
Figure 2.
Preparation and characterization of EV-coated multi-antigenic nanovaccines. (A) Representative TEM images of MSN (I, scale bar: 100 nm), ICG/MSN (II, scale bar 100 nm), EV13/ICG/MSN (III, scale bar: 50 nm), EV15/ICG/MSN (IV, scale bar: 50 nm), EV26/ICG/MSN (V, scale bar: 50 nm) and a zoomed-in view of a single EV/ICG/MSN nanoparticle (VI, scale bar: 50 nm). (B) Hydrodynamic size (diameter, nm), PDI and (C) zeta potential of MSN, ICG/MSN, EV13/ICG/MSN, EV15/ICG/MSN and EV26/ICG/MSN. (D) Quantification of protein concentrations of nanovaccines before and after membrane coating. (E) Absorption spectra of MSN, ICG, ICG/MSN. (F) Absorption spectra of EV-coated hybrid nanovaccines. (G) Fluorescence spectra of MSN, ICG, ICG/MSN. (H) Fluorescence spectra of EV-coated hybrid nanovaccines. (I) Solution temperature changes after exposure to laser irradiation. (J) Size changes of MSN, ICG/MSN and EV-coated nanovaccines in PBS buffer. Data are presented as the means ± SD (n = 3).