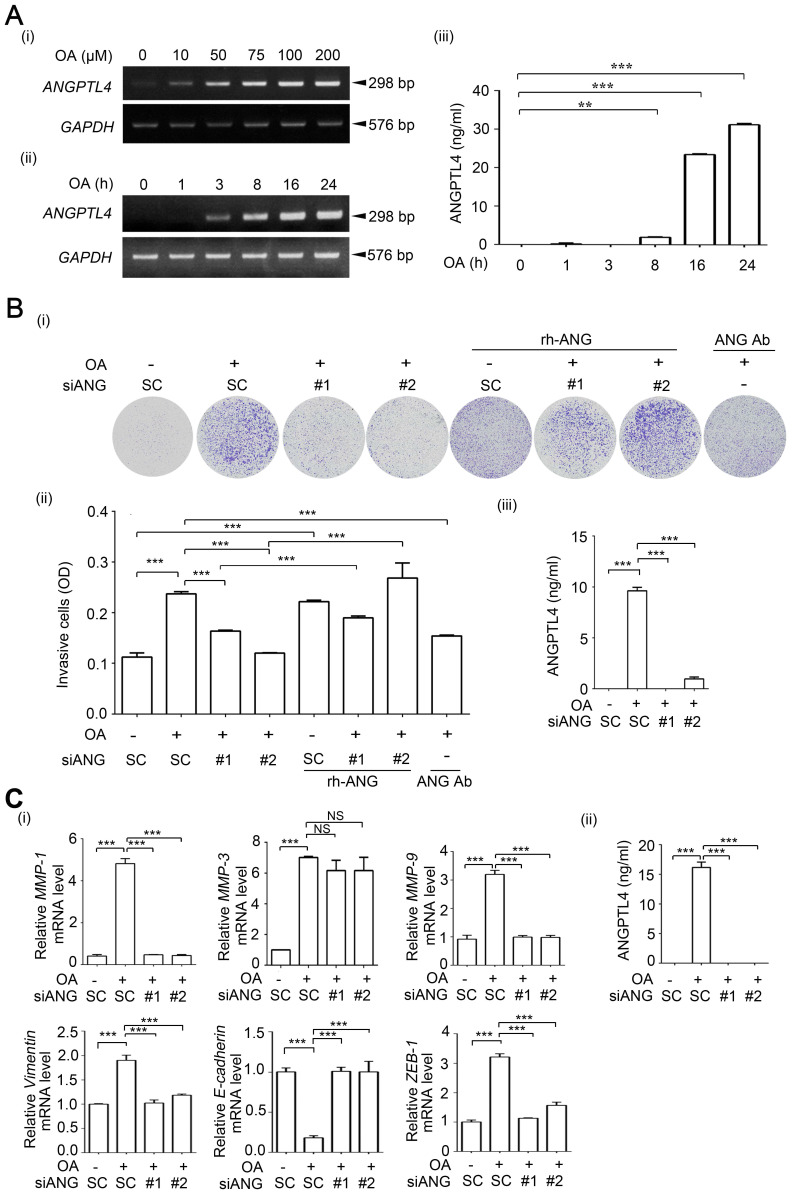
Figure 3.
OA-induced secretion of ANGPTL4 enhances invasion ability in cancer cells. (A) Semi-quantitative PCR analysis was performed to examine ANGPTL4 mRNA levels in SW480 cells treated with OA at various concentrations (i) or periods of time (ii), as indicated. ELISAs were performed to asses ANGPTL4 secretion levels (iii). (B) Invasion assays were performed using SW480 cells transfected with 20 nM ANGPTL4 siRNA (siANG#1 or #2) or scrambled oligonucleotides (SC) and then treated with 200 µM OA, 1 µg/ml anti-ANGPTL4 antibody (ANG Ab), and 100 ng/ml recombinant human ANGPTL4 (rh-ANG) for 72 h. Invading cells were stained with crystal violet and imaged under a microscope (i), and then solubilized with 10% acetic acid. The absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 595 nm (ii). ELISAs were performed to assess ANGPTL4 secretion in SW480 cells transfected with 20 nM siANGPTL4 or SC siRNA followed by treatment with 200 µM OA for 24 h (iii). (C) Real-time quantitative PCR analysis of MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-9, Vimentin, E-cadherin, and ZEB-1 mRNA levels was performed in SW480 cells transfected with 20 nM siANGPTL4 or SC siRNA and then treated with 200 µM OA for 16 h (i). ELISAs were performed to assess ANGPTL4 secretion (ii). The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. P-values were determined using a two-tailed Student's t-test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (n=3).