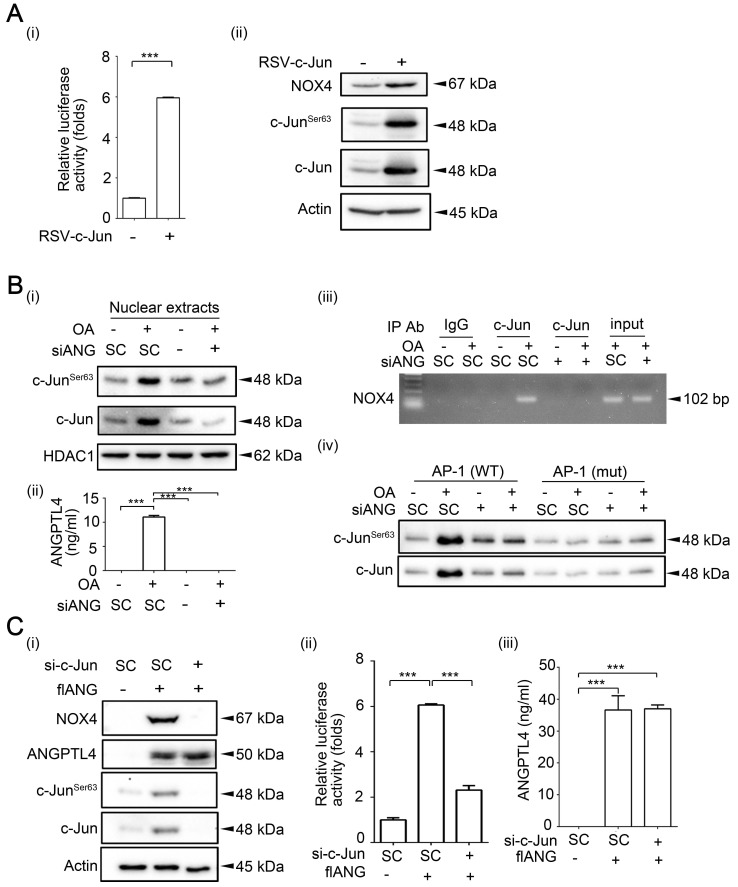
Figure 6.
c-Jun expression is essential for OA- and ANGPTL4-induced NOX4 transcriptional activity. (A) Dual-luciferase reporter assay was performed to analyze the activation of NOX4 promoter in SW480 cells transfected with the RSV-c-Jun expression vector for 24 h. Firefly luciferase activity was determined and normalized to Renilla luciferase activity (i). Immunoblot analysis of cell lysates form SW480 cells was performed using anti-phospho-c-JunSer63, anti-c-Jun, anti-NOX4, and anti-actin antibodies (ii). (B) Immunoblot analysis was performed using antibodies against HDAC1, c-Jun and phosphor-c-JunSer63 from SW480 cells transfected with 20 nM siANGPTL4 followed by treatment with 200 µM OA for 16 h (i). The secretion of ANGPTL4 was determined by ELISAs (ii). Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay (iii) and DNA affinity precipitation assay (iv) were performed to examine the binding of c-Jun to the NOX4 promoter with wild-type (WT) and mutated (mut) AP-1 sites in SW480 cells transfected with 20 nM siANGPTL4 followed by treatment with 200 µM OA for 16 h as described in “Materials and methods”. (C) Protein levels of ANGPTL4, NOX4, c-JunSer63, c-Jun, and actin, NOX4 promoter activity, and the secretion of ANGPTL4 were determined by Immunoblot analysis (i), dual-luciferase reporter assay (ii) and ELISAs (iii) in cells transfected with 20 nM c-Jun siRNA (si-c-Jun) and expression vector of ANGPTL4 (flANG). The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. P-values determined using a two-tailed Student's t-test. ***P < 0.001 (n=3).