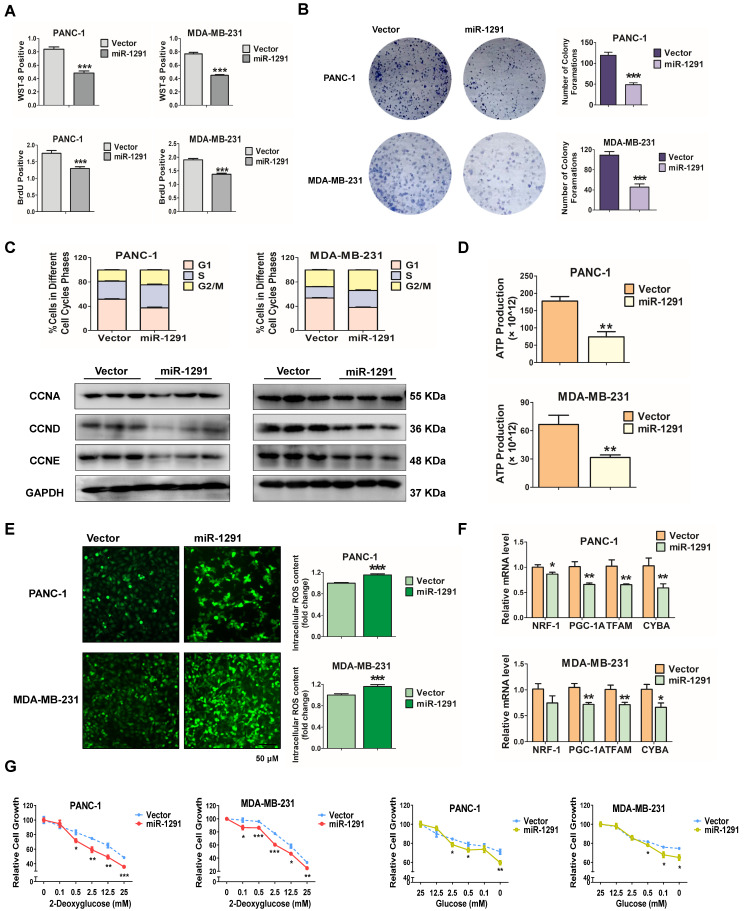
Figure 1.
miR-1291 inhibits cancer cell proliferation and metabolism. (A) A WST-8 assay was performed to examine the viability of PANC-1 and MDA-MB-231 cells after overexpression of miR-1291. BrdU activity was used to measure cell proliferation capacity after treated with miR-1291 plasmid. Data are mean ± SD (n = 5). (B) For colony formation assays, the cells were stained with Diff-Quik after being cultured for an additional 14 days. (C) The cell cycle was determined by flow cytometry after transfection with miR-1291 and immunoblot analysis of cell cycle-related proteins, such as cyclin A/D/E after transfection with miR-1291. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). (D) ATP production in miR-1291-transfected cells. Data are mean ± SD (n = 5). (E) Intracellular accumulation of ROS in two cell lines. Data are mean ± SD (n = 5). (F) RT-qPCR analysis to determine the expression of the mitochondriogenesis-related NRF1, PGC-1A, TFAM, and CYBA mRNAs. Data are mean ± SD (n = 6). (G) Glycolysis inhibition test with 2-deoxyglucose and a glucose deprivation test with glucose to measure the anti-metabolic stress ability of cells. Data are mean ± SD (n = 5).