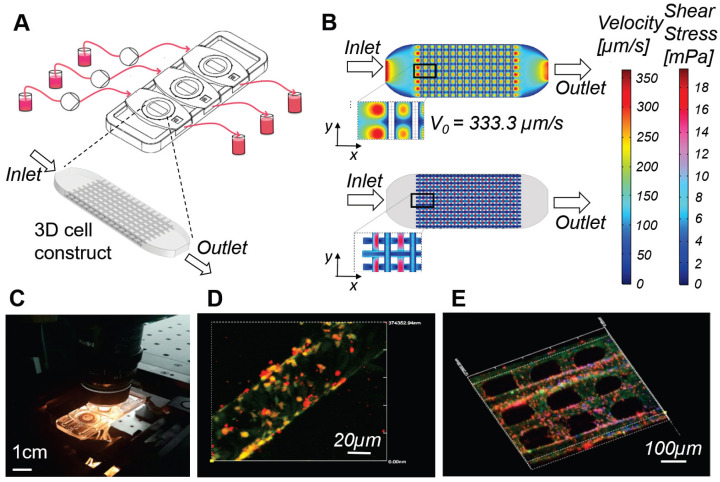
Figure 3.
Millifluidic optically accessible bioreactor (MOAB) for perfused culture of 3D cell constructs. A) The system is composed of, from left to right: culture medium reservoirs, microfluidic pumps, bioreactor chamber and reservoirs for medium collection. CAD model of the 3D cell construct or organoid, cultured in the culture chambers, used for numerical simulations. B) Results of the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations for a single culture chamber of the system. Top: fluid velocity (modulus of the velocity vector) is mapped on the whole culture chamber. Bottom: wall shear stress (WSS) is computed and mapped at the cell-culture medium interface. C) Photo of the MOAB showing the three independent chambers connected to the perfusion chamber by oxygenator tubes; the device is placed on a confocal microscope connected to a CPU allowing real time imaging of a perfused lymph-node-on-a-chip model, for the development and testing of vaccines and agents for cancer immune-therapy. D) Fibroblast reticular cells (yellow) are seeded on the 3D fiber scaffold. Dendritic cells introduced in suspension during culture medium flow adhere to the fibroblast reticular cells, migrate to the scaffold, and are activated to express the adhesion receptor ICAM-1 (red). E) Antigen-specific T cells (cyan) introduced with culture medium flow tend to adhere to dendritic cells expressing ICAM-1 (red) while crawling on the scaffold.