Figure 4.
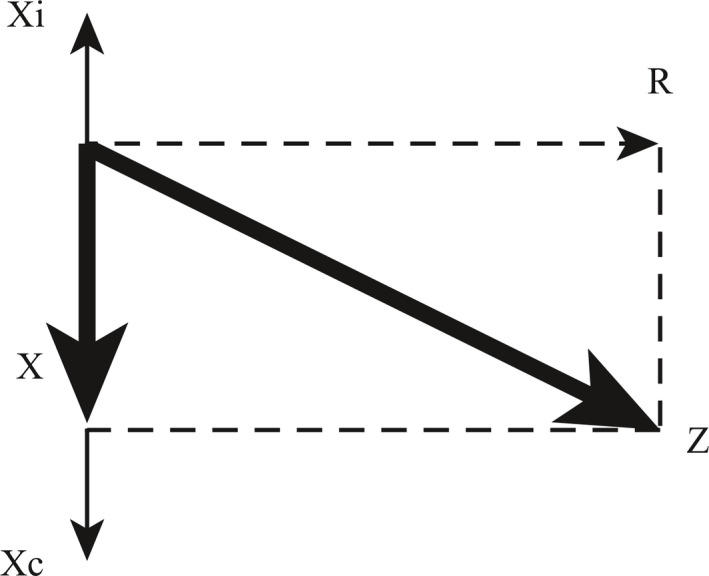
Planar representation of phase relationships between resistive (R), elastic/compliant (Xc) and inertive pressures (Xi). The arithmetic sum of elastic and inertive pressure at any given moment is termed the “reactance,” X. X is 90 degrees out of phase with R. The total impedance, Z, is the vector sum of the reactance and resistance, and has both a magnitude and a phase angle.
