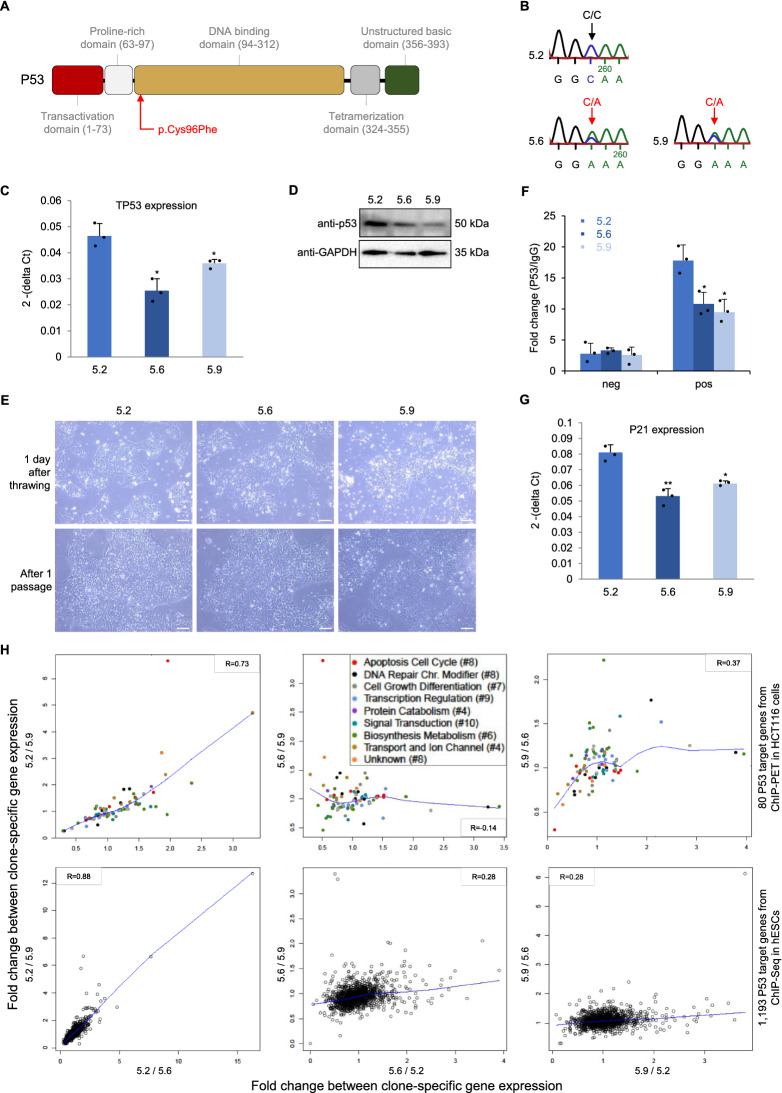
Figure 3.
Somatic mutation in TP53 in iPSC clones of patient TOF-02. (A) Multifunctional domains of P53 (adapted from Robbins et al.38). The identified rare damaging SNV is located in the highly conserved DNA-binding core domain. (B) Sanger sequencing results. (C) Expression of TP53 in the individual iPSC clones of TOF-02 measured using quantitative real-time PCR. Expression was measured in triplicates and normalized to HPRT. (D) The protein level of P53 in the individual iPSC clones of TOF-02. GAPDH was used as the internal control. The grouping of gels/blots cropped from different parts of the same gel. Uncropped blots are available in Supplementary Fig. S10. (E) The comparison of TOF-02 iPSC morphology. The cells were maintained and propagated in E8 medium. Scale bar 240 µm. (F) The relative fold change of P53 enrichment between P21 positive region and negative region. (G) Expression of P21 in the individual iPSC clones of TOF-02 measured using quantitative real-time PCR. Expression was measured in triplicates (n = 3) and normalized to GAPDH. Significance was tested using a two-sided t-test. (H) Fold changes between clone-specific gene expression values of P53 target genes from ChIP-Seq in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) and from ChIP-PET in HCT116 cells. The blue line indicates the locally-weighted polynomial regression (lowess fit). R: Pearson correlation; SNV: single nucleotide variation; TPM: transcripts per kilobase million. *P-value < 0.05.