Fig. 1.
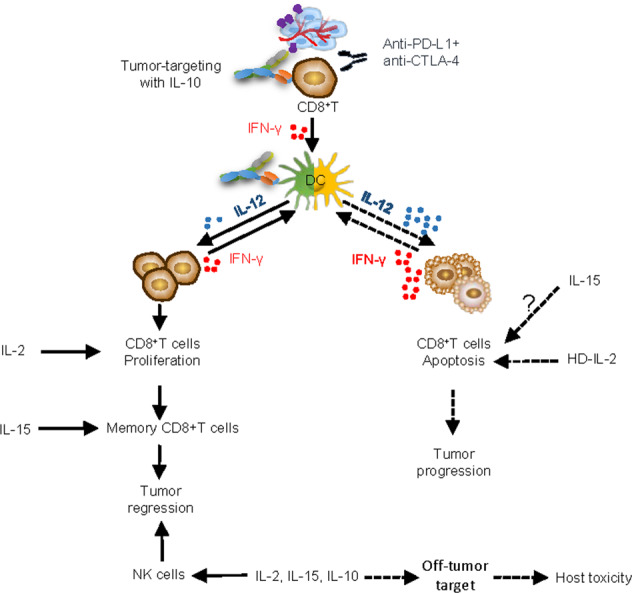
Distinct and cooperative roles of IL-10, IL-2, and IL-15 in antitumor immunity. Tumor-targeted delivery of IL-10 inhibits intratumoral CD8+ T-cell apoptosis, which may offer a strong rationale for combining IL-10-based strategies with immunotherapies that can potently boost T-cell proliferation and function, such as IL-2 and immune checkpoint blockade therapy, and the addition of IL-15 may further boost NK and memory CD8+ T-cell immunity to achieve synergistic antitumor effects. Nontargeted delivery of cytokines induces host toxicity, limiting the therapeutic index
