Figure 1:
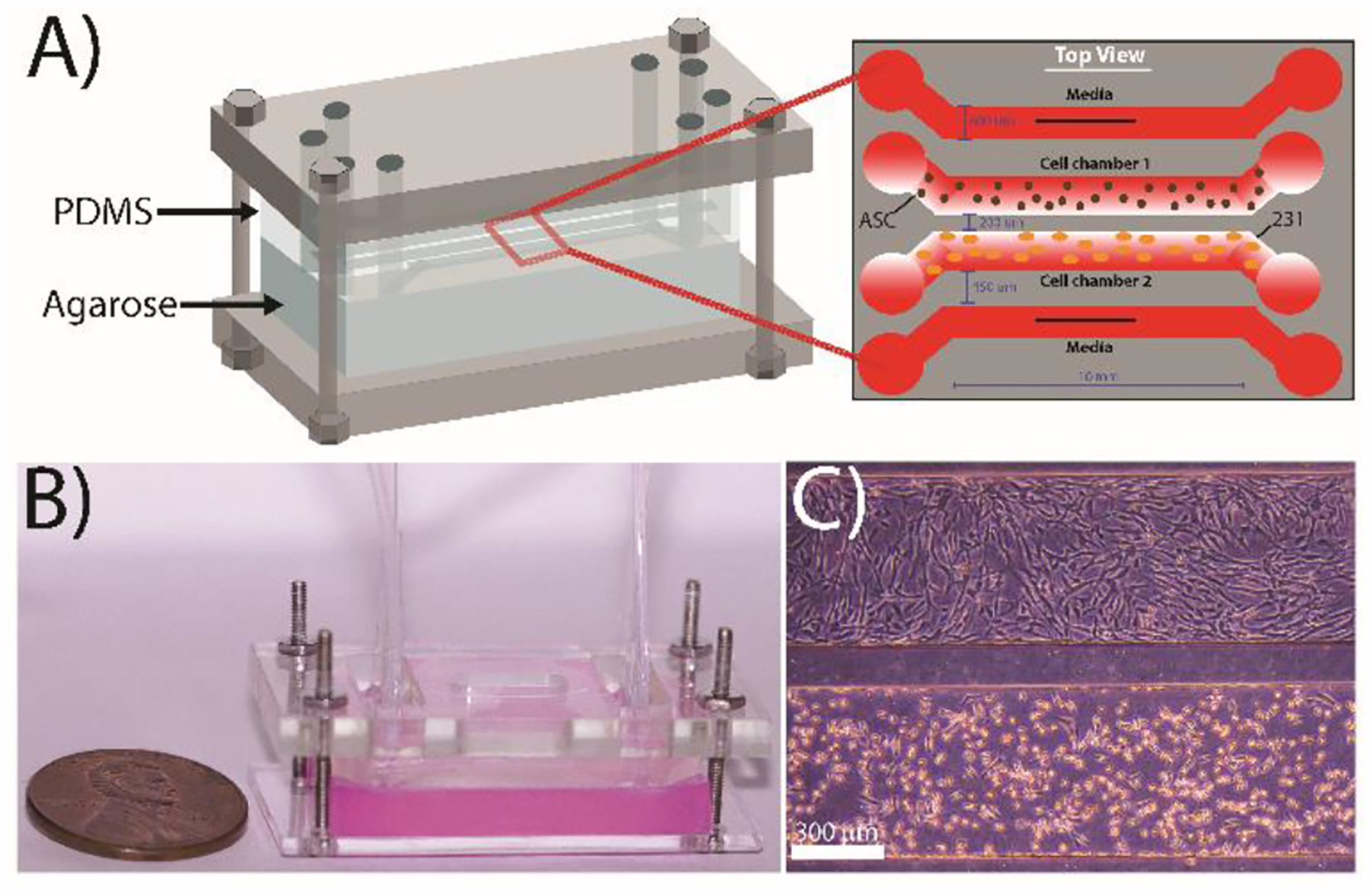
Design of the microfluidic co-culture device. (A) The flow-free microfluidic device consisted of four fluidic channels imprinted into a PDMS slab placed on top of 3 wt% agarose. The device contains four parallel channels: the two outermost ‘flow’ channels are constantly supplied with media while the two innermost “flow-free” channels are used to culture the MDA-MB-231 cells and adipose stem cells. All channels are 600 μm wide with a contact length of 10 mm and a height of 150 μm. The spacing between the media channels and the culture channels is 450 μm, while the spacing between the two cell culture channels is 200 μm to facilitate cellular crosstalk. (B) Image of a completely assembled device with agarose stained red for enhanced visualization. (C) Representative image of MDA-MB-231 cells (bottom) and ASCs (top) cultured in the device after 72 h.
