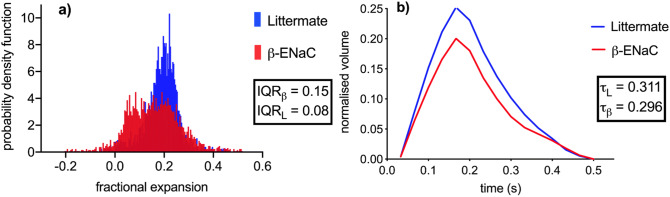
Figure 2.
Comparative lung expansion analysis for a β-ENaC (M3, red) and littermate (M9, blue) pair of mice. (a) A histogram analysis of the fractional tissue displacement for the littermate and β-ENaC mice from Fig. 1, with the interquartile ranges of the normalised histogram shown as IQR. Note that Fig. 1 shows a single coronal slice, whereas the histogram is calculated from the entire volume. The fractional expansion for the β-ENaC mouse has a split peak. (b) The volume/time curve over the course of the ~ 0.5 s breath for the entire lung provides a global measurement of lung health. The volume of air breathed throughout the breath is expressed as a fraction of the entire lung volume; fractional volume. The healthy mouse breathes more air relative to the size of its lung. From this we can calculate the global expiratory time constant (τ).