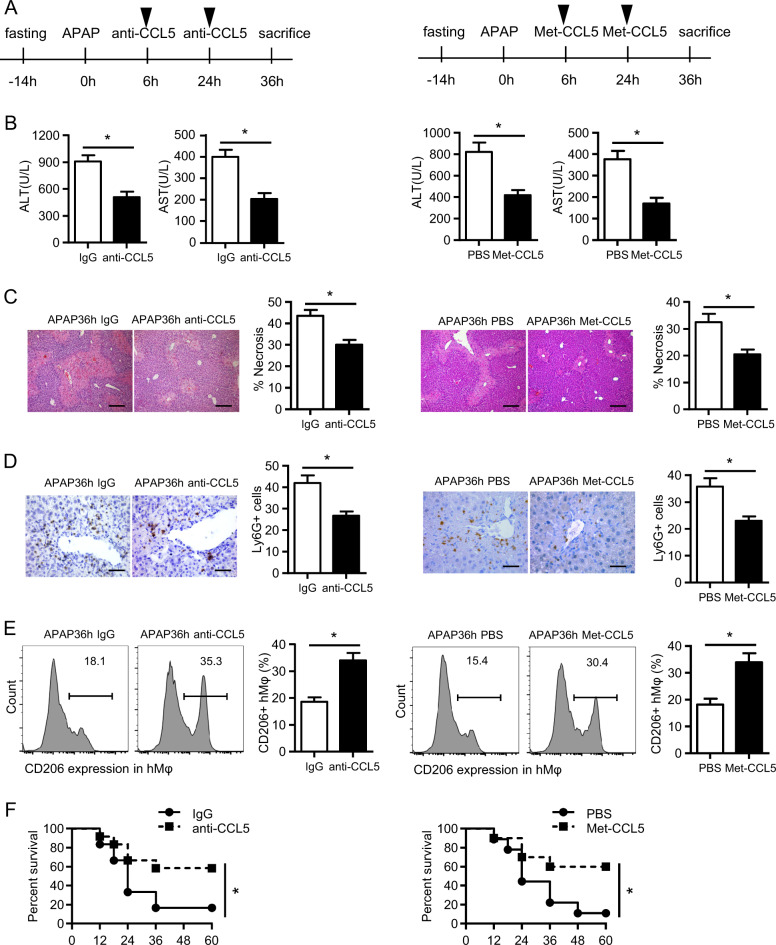
Fig. 7.
CCL5 neutralization or inhibition facilitates liver recovery after acute liver injury. a A schematic of CCL5 inhibition by anti-CCL5 or Met-CCL5 in the APAP overdose model. The dose of anti-CCL5 and Met-CCL5 was 10 μg. b Serum levels of ALT/AST were detected after anti-CCL5- or Met-CCL5-mediated CCL5 blockage (n = 4–6). c Representative images of H&E staining (original magnification = ×100, scale bar = 200 μm) and the statistical quantification of hepatic necrosis upon anti-CCL5- or Met-CCL5-mediated CCL5 inhibition (n = 4–6). d Representative images and the statistical quantification of hepatic Ly6G+ cells in liver sections (original magnification = ×400, scale bar = 50 μm) upon anti-CCL5- or Met-CCL5-mediated CCL5 inhibition (n = 4–6). e Representative FACS plots and the statistical quantification of CD206+ hepatic macrophages (hMφ) upon anti-CCL5- or Met-CCL5-mediated CCL5 inhibition (n = 4–6). f Survival curves of mice (n = 10–12) in response to a lethal dose of APAP treatment upon anti-CCL5- or Met-CCL5-mediated CCL5 inhibition. The data are shown as means ± SEM, *P < 0.05