Fig. 1: Dietary fatty acid deficiency from birth results in a pronounced prolongation of the postnatal window of cardiomyocyte proliferation.
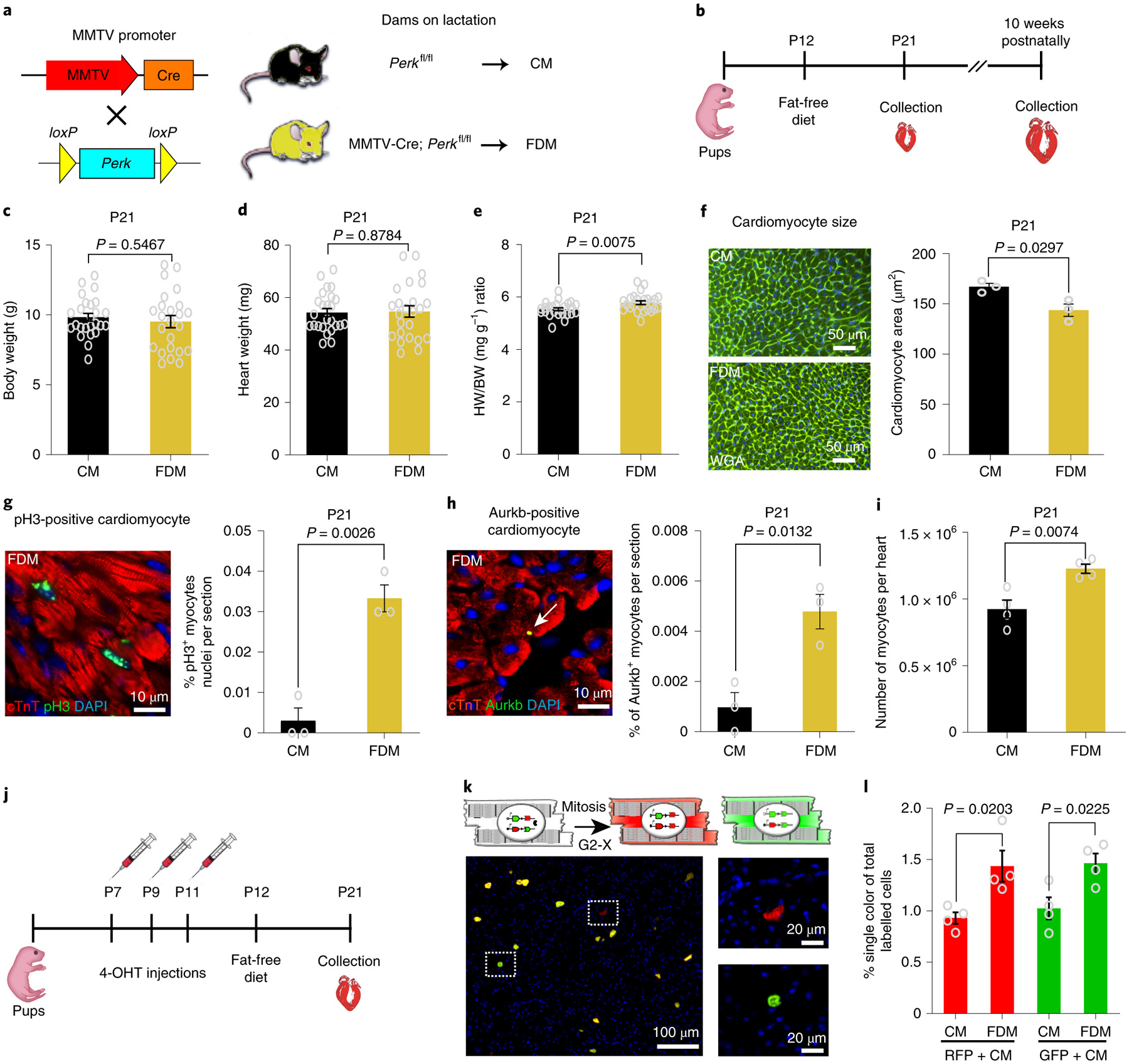
a, Schematic view of the genetic mouse model of PERK deletion specifically in mammary epithelial cells. The Cre+/PERKf/f mice produce milk deficient in fatty acids. As a control, we used the Cre−/PERKf/f mice, which produce milk with normal levels of fatty acids. b, At 12 days postnatally, beyond lactation, pups were exposed to a regular diet or Fat Free Diet. Animals were sacrificed at 21 days or 10 weeks postnatally. c, Body weight (BW) measurements show no significant difference between FDM (n=24 biologically independent mice) and CM (n=25 biologically independent mice). d, Heart weight (HW) measurements showing no difference between groups; n=24 biologically independent mice for FDM group and n=25 biologically independent mice for CM group. e, Heart weight to body weight (HW/BW) ratio shows a significant increase in FDM (n=24 biologically independent mice) compared to CM (n=25 biologically independent mice). f, WGA staining shows a significant decrease in cardiomyocyte cell size measurement in FDM compare to CM (n=3 biologically independent mice per group). g, Anti-pH3 and anti-cTnT co-immunostaining showing a significant increase in the cardiomyocyte mitosis marker in the FDM group (n=3 biologically independent mice per group). h, Anti-Aurora B kinase and anti-cTnT co-immunostaining shows a significant increase in the cardiomyocyte cytokinesis marker in the FDM compared to the CM group (n=3 biologically independent mice per group). i, A complete dissociation of cardiomyocytes by collagenases indicated a significant increase in the total number of cardiomyocytes in FDM group compared to CM (n = 4 biologically independent mice). j, Schematic view of 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) administration and timeline experiment in MADM; MCM mice. k, (Upper) Schematic representation of MADM; MCM recombination in a parent cardiomyocyte leading to RFP+ and GFP+ single-labeled daughter cardiomyocytes. (Lower) Example of RFP+ and GFP+ single-labeled cardiomyocyte. l, Frequency of single-labeled cardiomyocytes per heart section are higher in the FDM group compared with the CM group (n=4 biologically independent mice per group). Data in bar graphs are presented as mean±s.e.m. Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed Student’s t-test: NS, not significant CM, control milk group; FDM, fat deficient milk group.
