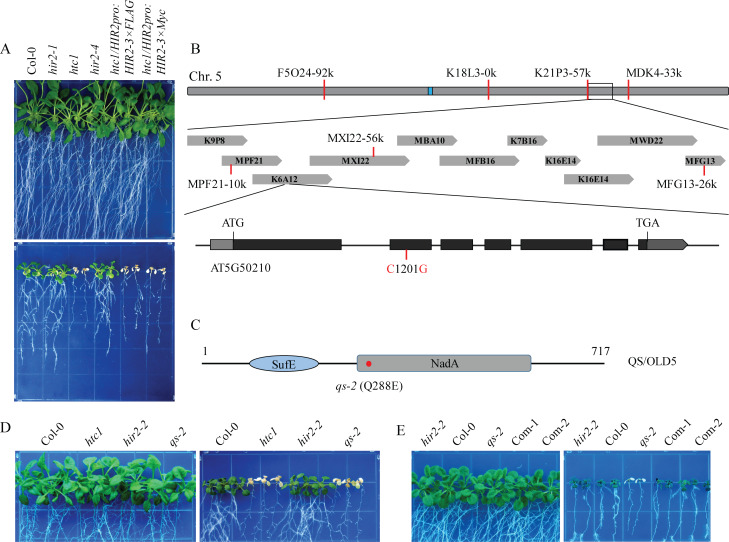
Fig 1. Identification of the HTC1/QS gene.
(A) The htc1 mutant plants displayed hypersensitivity to chilling stress. Seven-day-old seedlings of Col-0, hir2-1, htc1, hir2-4, and two transgenic lines grown on 1/2 MS medium plates were transferred to a growth chamber at 22°C (upper) or 4°C (bottom) for an additional 21 days. (B) Map-based cloning of the qs-2 mutation. A total of 96 samples were used for rough genetic mapping which narrowed the htc1 mutation to the region between the BAC clones MPF21-10k and MXI22-56k on chromosome 5. An C to G mutation in the second exon of AT5G50210 was identified by genome re-sequencing. (C) The structure of QS protein. SufE, Fe-S metabolism associated domain; NadA, quinolinate synthase domain. The position of the Q288E substitution in the qs-2 mutant is indicated by a red dot. (D) Chilling sensitivity of the qs-2 mutant. Seven-day-old seedlings of Col-0 wild-type, htc1 and its segregated alleles hir2-2, qs-2 grown on 1/2 MS medium plates at 22°C (left) or 4°C (right) for 21 days. (E) Molecular complementation assay of the chilling hypersensitive phenotype of qs-2 mutant. Seven-day-old seedlings of Col-0 wild-type, qs-2 and two complementation lines were grown on 1/2 MS medium at 22°C (left) or 4°C (right) for 21 days.