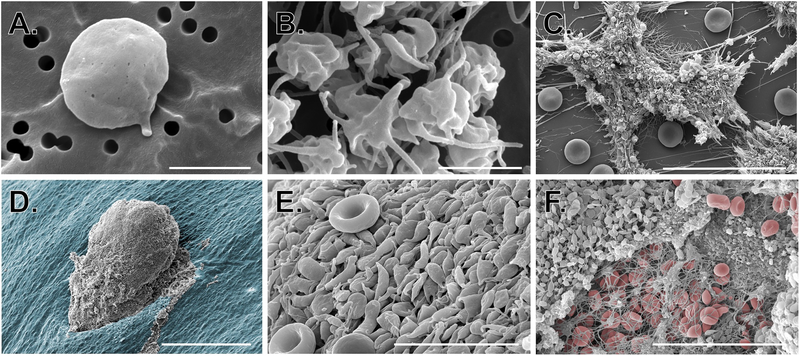
Figure 2: Use of SEM to study platelets in vitro and in vivo.
SEM images show A-B) isolated resting and activated human platelets (scale bars = 2 μm); C) human platelet-rich thrombi formed in a microfluidic flow chamber coated with collagen and tissue factor (scale bar = 30 μm); D-F) platelet-rich hemostatic plugs formed following puncture injury to a mouse jugular vein. D) hemostatic plug imaged from the intraluminal side (scale bar = 150 μm); the endothelium is pseudocolored blue. E) High magnification image of platelets on the luminal surface of a hemostatic plug (red blood cells can be seen for comparison; scale bar = 10 μm). F) Extraluminal component of a hemostatic plug showing platelets, fibrin and a few fibrin entrapped red blood cells (RBCs are pseudocolored red, scale bar = 30 μm). Image credit: M. Tomaiuolo and T.J. Stalker.