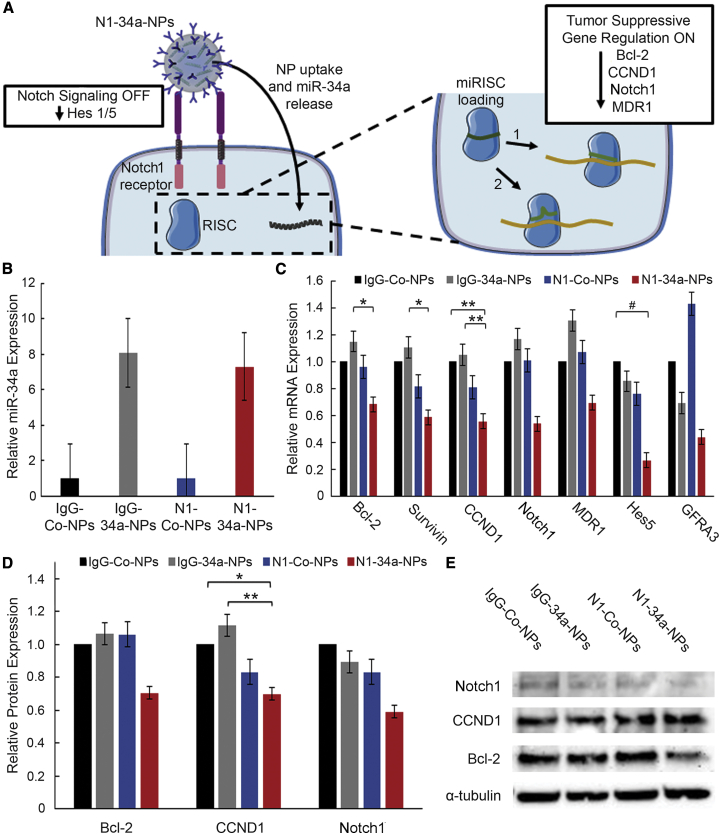
Figure 2.
Nanoparticle Interaction with TNBC Cells and Evaluation of Gene Regulation
(A) Scheme of posited NP interaction with MDA-MB-231 TNBC cells. Upon cellular binding (see also Figure S1), N1-34a-NPs inhibit downstream Notch signaling through antibody-mediated signal cascade interference and also deliver miR-34a, which reduces the expression of several genes by guiding the RNA-induced silencing complex (miRISC) to targeted mRNA sequences with perfect (1) or imperfect (2) complementarity, resulting in mRNA degradation or translational repression. (B) Real-time qRT-PCR analysis of relative miR-34a levels after treatment with IgG-Co-NPs, IgG-34a-NPs, N1-Co-NPs, or N1-34a-NPs (n = 3). U6 was used as a control, and relative expression is normalized to that of cells treated with IgG-Co-NPs. Error bars indicate standard error. (C) Real-time qRT-PCR analysis of relative Bcl-2, survivin, CCND1, Notch1, MDR1, GFRA3, and Hes5 mRNA expression after treatment with IgG-Co-NPs, IgG-34a-NPs, N1-Co-NPs, or N1-34a-NPs (n = 3). GUSB was used as a control, and relative mRNA expression is normalized to that of cells treated with IgG-Co-NPs. Error bars indicate standard error. #p < 0.1, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01. (D) Quasi-quantitative analysis of western blotting for normalized Bcl-2, CCND1, and Notch1 protein expression (n = 3). α-Tubulin was used as a control, and expression was normalized to expression in cells treated with IgG-Co-NPs. Error bars indicate standard error. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01. (E) Representative western blot bands for Bcl-2, CCND1, Notch1, and α-tubulin protein levels. Bands are from a single blot that was stripped and probed for multiple targets.