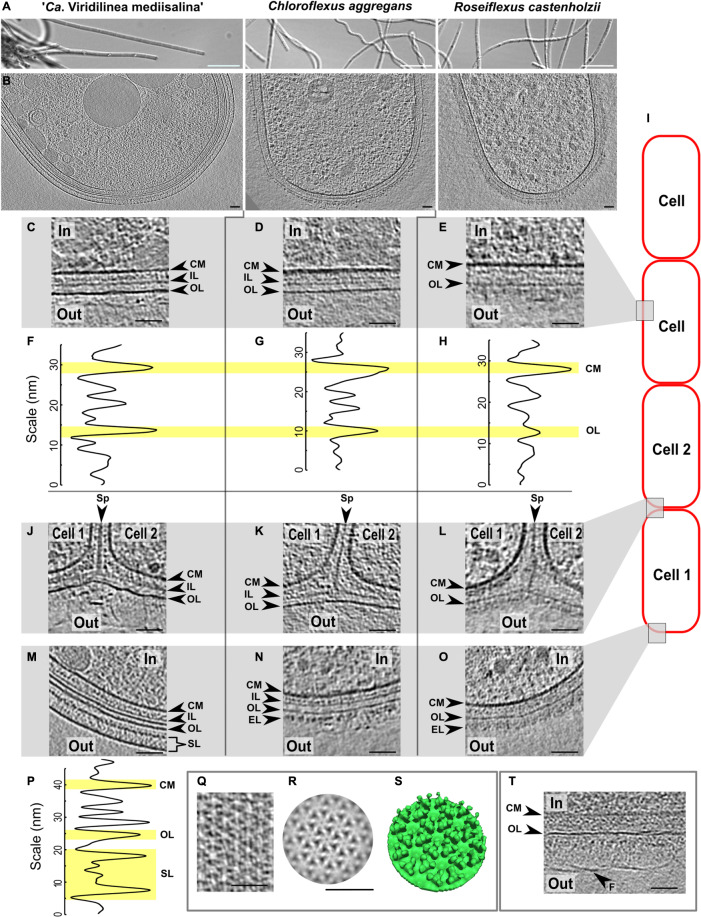
FIGURE 1.
Comparative cryo-ET of the cell envelope of the Chloroflexales bacteria. Morphology of the strains in a light microscope (A). Slices through tomograms of a terminal cell in the multicellular filaments (B). Slices through tomograms of a middle part of the cells in “Ca. Viridilinea mediisalina” (C), C. aggregans (D), R. castenholzii (E). Density profile of the cell envelope on the middle part of the cells in “Ca. Viridilinea mediisalina” (F), C. aggregans (G), R. castenholzii (H). Slices through tomograms of a cell-cell junctions in “Ca. Viridilinea mediisalina” (J), C. aggregans (K), R. castenholzii (L). Slices through tomograms of an apex of the terminal cells in “Ca. Viridilinea mediisalina” (M), C. aggregans (N), R. castenholzii (O). Density profile of the cell envelope in the apex of the “Ca. Viridilinea mediisalina” terminal cell (P). S-layer on tomogram without cryo-FIB (Q). Sub-tomogram averaging of the S-layer (R) and its isosurface (S). Fibrillar layer on a middle part of the cells in “Ca. Viridilinea mediisalina” (T). In, cytoplasm in a cell; out, extracellular space; CM, cytoplasmic membrane; EL, external layer; FL, fibrillar layer; F, fibrils; IL, intermediate layer; OL, outer layer; SL, S-layer; Sp, septum. Bars: 10 μm (A), 50 nm (B–T). Scheme of the bacterial multicellular filament (I).