Fig. 2.
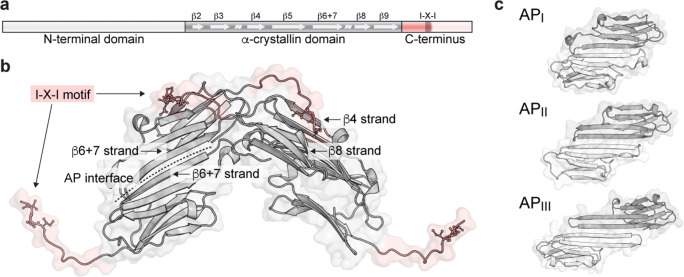
Structural regions of sHSPs and hierarchy of assembly. a. The primary sequence encodes three domains: a central β-sheet rich ACD flanked by N- and C-terminal regions. Truncating the termini (faded regions) reduces polydispersity and facilitates crystallization. b. X-ray structure of the HspB5 ACD and partial C-terminus, showing 4 monomers (Laganowsky et al. 2010). The ACD dimerizes via an antiparallel (AP) interface between strands β6 + 7. The C-terminus bridges dimers by docking into a groove between strands β4 and β8 via the I-X-I motif (sticks; in HspB5, X = proline). c. The contacts comprising the AP interface may shift under different conditions, evidenced by the observation of three registers of the HspB5 dimer by X-ray crystallography (PDB IDs 3L1G, 2WJ7, 4M5S). Multiple registers of the HspB1 ACD dimer have also been captured in X-ray structures (H. Gastall, unpublished)