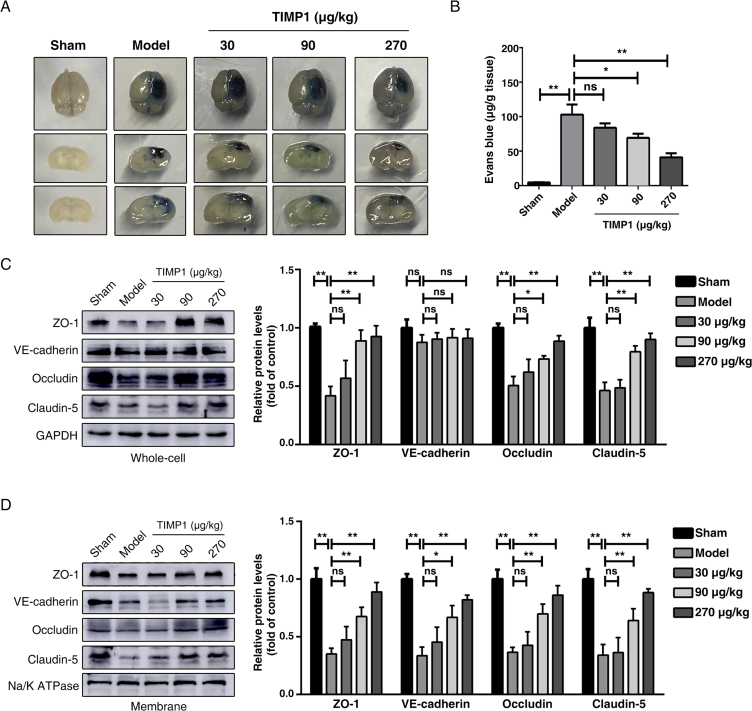
Figure 2.
rTIMP1 treatment attenuates blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeability and loss of junctional proteins (JPs) in TBI mice. (A) Representative images of brain tissues and corresponding coronal sections from sham injury group, TBI group treated with vehicle or TBI groups treated with rTIMP1 (30, 90, and 270 μg/kg, i.v.) at 3 days after traumatic brain injury. Blue area indicates extravasation of Evans blue dye. (B) Quantification of the Evans blue dye contents leaking into the ipsilateral cerebral hemisphere tissue of mice from the indicated treatment groups (n = 11–12 per group). (C) Western blot analysis and quantification of ZO-1, VE-cadherin, occludin and claudin-5 in ipsilateral hemispheric brain total lysates from the indicated treatment groups at 72 h post-TBI. GAPDH was used as loading control. n = 5 per group. (D) Western blot analysis and quantification of ZO-1, VE-cadherin, occludin and claudin-5 in ipsilateral hemispheric brain membrane fragments from the indicated treatment groups at 72 h post-TBI. Na/K ATPase was used as loading control. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM, n = 5 per group. (ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).