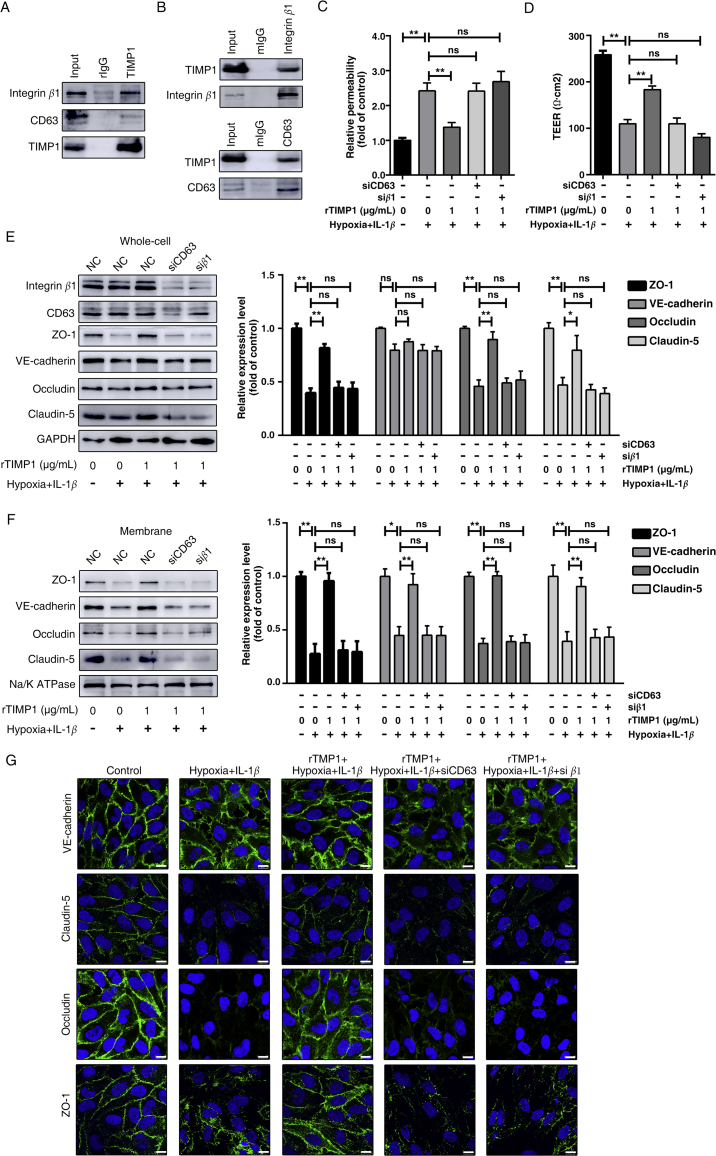
Figure 6.
TIMP1 modulates BBB integrity through CD63 and integrin β1 signaling. (A) Total cell lysates from HBMECs were extracted and subjected to IP assay using TIMP1 antibody. Western blots were performed for integrin β1, CD63 or TIMP1. (B) Total cell lysates from HBMECs were extracted and subjected to integrin β1 or CD63 IP assays. This was followed by Western blot analysis for integrin β1, CD63 or TIMP1. (C)–(H) HBMECs transfected control or siRNA targeting CD63 or integrin β1 were treated with rTIMP1, then the indicated groups were subjected to hypoxia plus 20 ng/mL IL-1β for 24 h. (C) HBMECs from the indicated treatment groups were subject to transwell permeability assay. Data represent mean ± SEM of six independent experiments (ns, not significant; **P < 0.01). (D) HBMECs from the indicated treatment groups were subject to TEER assay. Data represent mean ± SEM of six independent experiments (ns, not significant; **P < 0.01). (E) Western blot analysis and quantification of indicated proteins from total cell lysates (ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). (F) Western blot analysis and quantification of indicated proteins from membrane fragments. Data represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments (ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). (G) Cells were also subjected to IF staining of VE-cadherin, claudin-5, occludin and ZO-1. Scale bars, 10 μm.