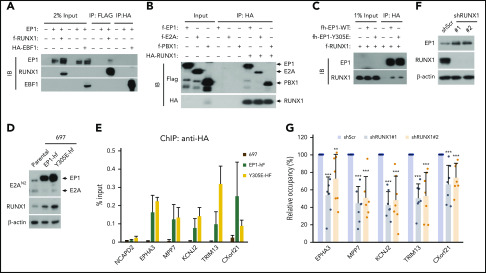
Figure 2.
RUNX1 interacts directly with and mediates the DNA binding of E2A-PBX1. (A) Co-IP assays showing an interaction between E2A-PBX1 and RUNX1, but not EBF1, in transfected HEK293T cells. Immunoprecipitations were conducted with anti-FLAG or anti-HA beads, and bound proteins were visualized by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. (B) Direct RUNX1 interactions with E2A-PBX1, E2A, and PBX1. Immunoprecipitation with purified proteins and anti-HA antibody followed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. (C) Co-IP assay showing RUNX1 binding to E2A-PBX1 WT and to a DNA-binding defective Y305E mutant. (D) Immunoblot showing the expression of exogenous EP1-hf and RUNX1 in stable 697 cells expressing E2A-PBX1 WT or Y305E mutant. (E) ChIP-qPCR of E2A-PBX1 WT or Y305E mutant at enhancers of indicated genes in stable 697 lines. (F) Immunoblot of endogenous E2A-PBX1 and RUNX1 in shScr- or shRUNX1-treated 697 lines. (G) ChIP-qPCR of E2A-PBX1 (HA) at enhancers of indicated genes in stable 697 line treated with shScr or shRUNX1. ChIP signals (y-axis) from 3 independent experiments, with 2 or 3 replicates, were compared with control (Scramble) and are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD).