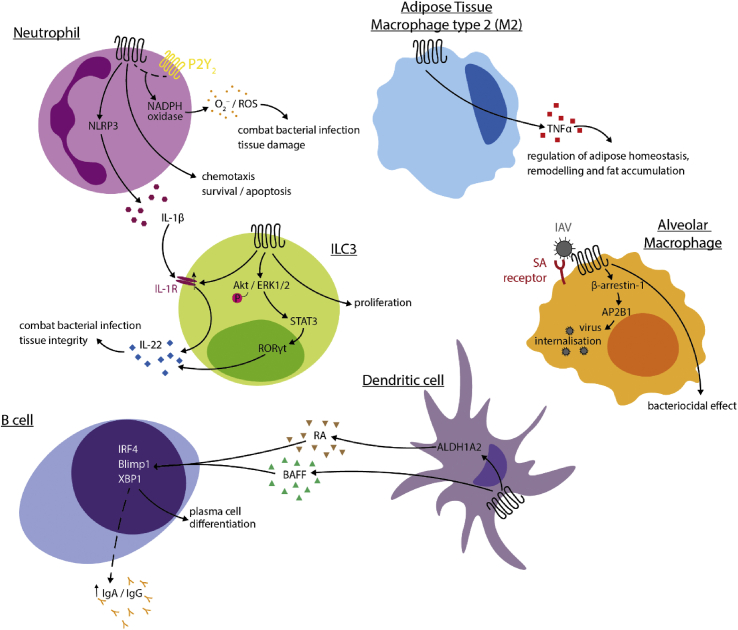
Figure 2.
Roles of FFA2 in immune cell populations. In neutrophils, activation of FFA2 triggers chemotaxis and potentially promotes neutrophil survival or apoptosis, promotes superoxide production (in crosstalk with P2Y2R) and the production of the cytokine IL-1β. Complementing this action, in ILC3 cells, activation of FFA2 leads to an upregulation of IL-1R, which is in turn activated by IL-1β to produce IL-22. FFA2 activation also directly leads to IL-22 production via the Akt/ERK1/2- signal transducer and activator of transcription 3– RAR-related orphan receptor γ t axis in these cells. In dendritic cells, activation leads to the production of BAFF and A2ALD1a2, the latter of which catalyses the production of retinoic acid, which along with BAFF promotes B-cell differentiation into plasma cells. FFA2 may also be involved in IgA/IgG release via an unknown mechanism. Activation of FFA2 in type 2 macrophages promotes the release of TNFα, as well as bacteriocidal activity through an unknown pathway. FFA2 may also function as a coreceptor for the influenza A virus, triggering a β-arrestin-1-dependent internalisation of the virus. AKT, protein kinase B; ALDH1A2, aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family, member A2; AP2B1, AP-2 complex subunit beta; BAFF, B-cell activating factor; Blimp1, B-lymphocyte-induced maturation protein-1; ERK, extracellular signal–regulated kinase; IAV, influenza A virus; IgA, immunoglobulin A; IgG, immunoglobulin G; IL-1β, interleukin 1β; IL-22, interleukin-22; ILC3, type 3 innate lymphoid cells; IRF4, interferon regulatory factor 4; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NLRP3, NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein 3; P2Y2, P2Y purinoreceptor 2; RA, retinoic acid; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TNFα, tumour necrosis factor α; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; RORγt, RAR-related orphan receptor γ t; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SA, sialic acid; XBP1, X-box binding protein 1.