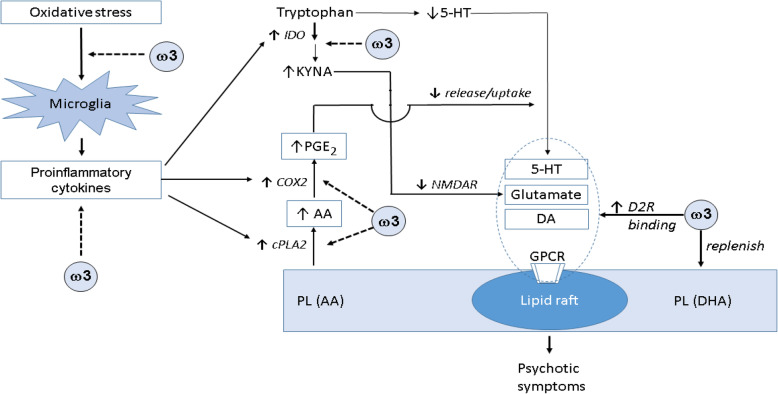
Fig. 2.
A scheme outlines mechanisms as how omega-3 fatty acids exert the beneficial effect on neurotransmission. Omega-3 fatty acids decrease oxidative stress; suppress formation of pro-inflammatory cytokines; inhibit production of KYNA, an antagonist of NMDA receptor, which increases glutamine levels; enhance release and uptake of serotonin, and facilitate dopamine binding to D2R by modulating membrane flexibility and permeability. Abbreviations: AA, arachidonic acid (20:4n-6); COX2, cyclooxygenase-2; DA, dopamine; DHA, docosahexaenoic acid (22:6n-3); D2R, dopamine receptor; 5-HT, serotonin, 5-hydroxytryptamine; KYNA, kynurenic acid; PGE2, prostaglandin E2