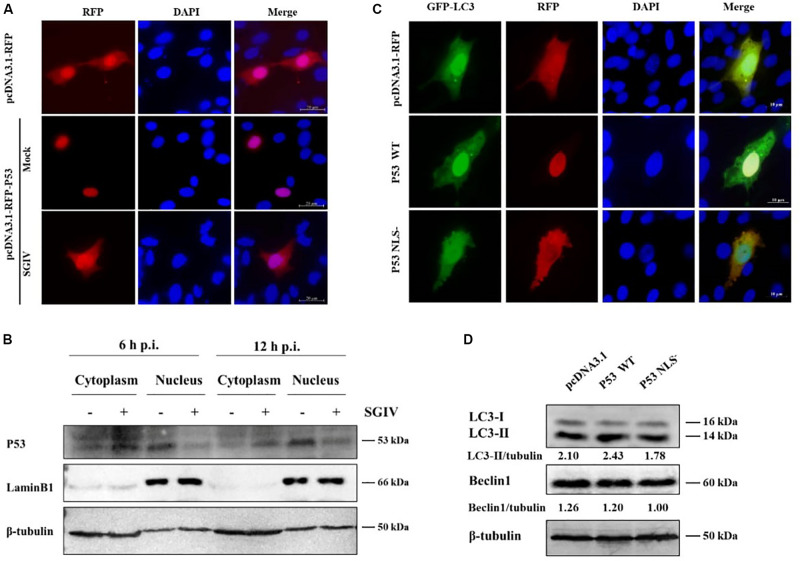
FIGURE 2.
SGIV increased cytoplasmic p53 level to inhibit autophagy. (A) SGIV infection altered the subcellular localization of p53. The transfected cells were fixed at 3 h p. i. (B) SGIV infection increased cytoplasmic p53 and decreased nuclear p53 levels. β-tubulin and LaminB1 were the internal references for cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts, respectively. (C) The cytoplasmic p53 (NLS–) reduced the clustering of GFP-LC3. pcDNA3.1-RFP, RFP-p53 WT, and RFP-p53 NLS– were co-transfected with GFP-LC3 plasmid into GS cells for 24 h, and stained with DAPI. (D) Subcellular localization of p53 affected the level of autophagy-related proteins. Band intensity was calculated and ratios of target protein/β-tubulin were assessed. The data were presented as the means from three independent experiment.