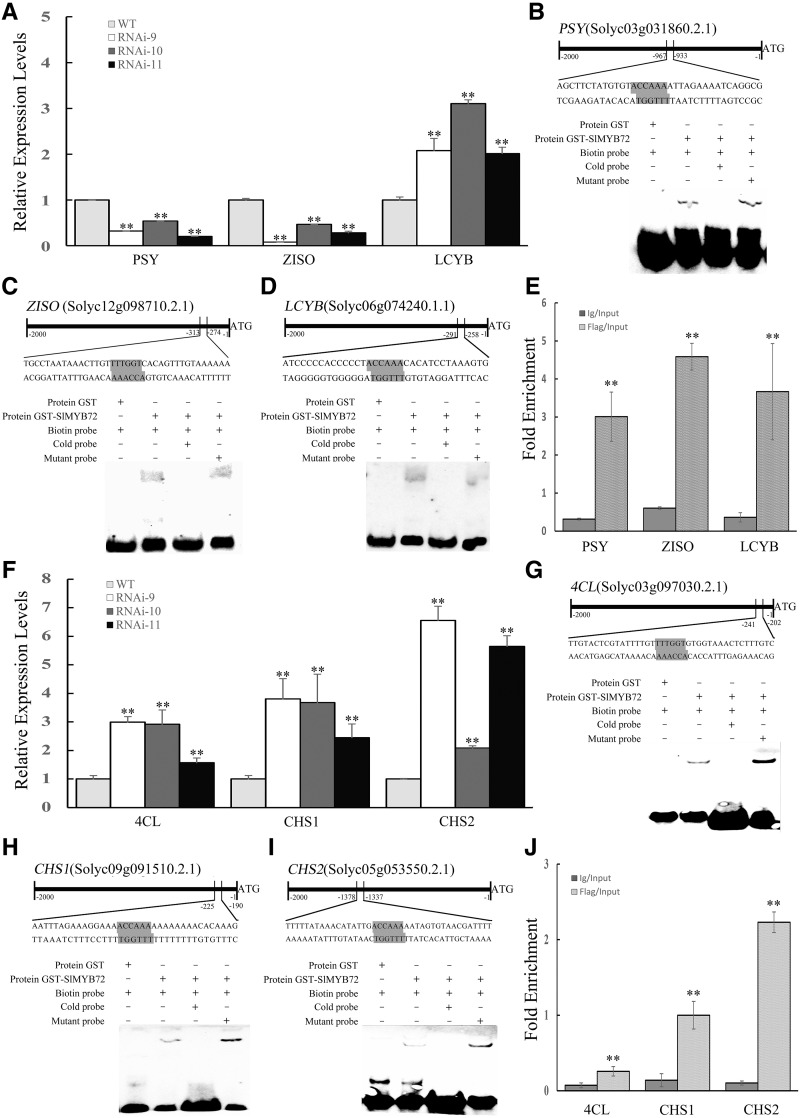
Figure 7.
SlMYB72 targets the genes involved in the biosynthesis of carotenoids and flavonoids. A, Expression levels of PSY, ZISO, and LCYB genes in pericarps of red fruits. RNAi, RNAi-SlMYB72 lines; WT, wild-type plants. The data represent means ± sd of four biological replicates. The relative expression levels of genes were compared between the RNAi-SlMYB72 and wild-type plants. B to D, EMSA showing the binding of SlMYB72 to the promoters of PSY, ZISO, and LCYB genes, respectively. Biotin-labeled DNA probes from native promoter or mutants were incubated with GST-SlMYB72 protein, and the DNA-protein complexes were separated on 6% native polyacrylamide gels. E, ChIP-qPCR assay for the direct binding of SlMYB72 to PSY, ZISO, and LCYB genes. Values are percentages of DNA fragments that coimmunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibodies or nonspecific antibodies (anti-IgG) relative to the input DNA. F, Expression levels of 4CL, CHS1, and CHS2 genes in pericarps of red fruit. G to I, EMSA showing the binding of SlMYB72 to the promoters of 4CL, CHS1, and CHS2 genes, respectively. J, ChIP-qPCR assay for the direct binding of SlMYB72 to the 4CL, CHS1, and CHS2 genes. The data represent means ± sd of four biological replicates in A, E, F, and J. Asterisks indicate significant differences between transgenic and wild-type plants (**P < 0.01), as determined by Student’s t test.