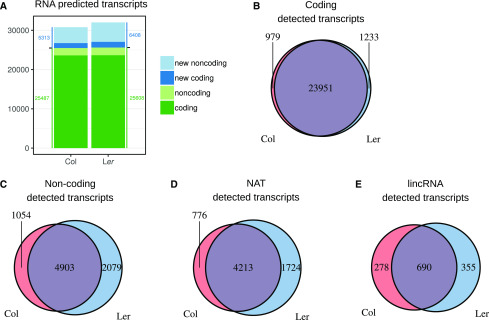
Figure 1.
Identification of the transcripts and their occurrence across the two ecotypes. A, Number of predicted coding and noncoding transcripts in the two ecotypes, classified by type. New transcripts refers to genes not characterized in previously published studies. B to E, Predicted transcripts in each ecotype were classified as coding (B) or noncoding (C). For the latter case, two subclasses are defined: antisense of another annotation (NAT; D) and intergenic (lincRNA; E). In contrast to coding genes, many noncoding RNAs, notably lincRNAs, were detected only in one ecotype despite the high DNA sequence similarity in both ecotypes.