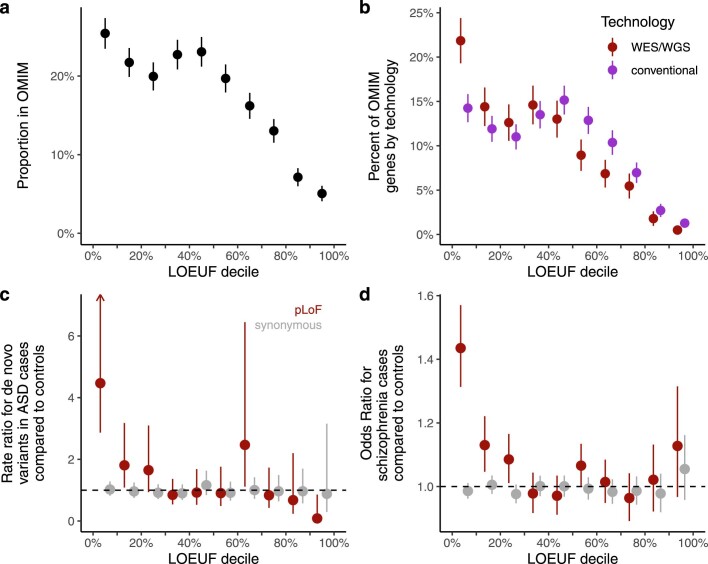
Extended Data Fig. 9. Applications of constraint metrics to rare variant analysis of disease.
a, Proportion of each LOEUF decile found in OMIM. b, Proportion of disease-associated genes discovered by whole-exome/genome sequencing (WES/WGS) compared to conventional (typically linkage) methods, plotted by LOEUF decile. The former are more constrained (LOEUF 0.674 versus 0.806, two-sided t-test P = 1.2 × 10−16), which suggests that these techniques are more effective for picking up genes with a de novo mechanism of disease, compared to recessive genes identified by linkage methods. c, Similar to Fig. 5a, the rate ratio is defined by the rate of de novo variants (number per patient) in autism cases divided by the rate in controls. pLoF variants in the most constrained decile of the genome are approximately fourfold more likely to be found in cases compared to controls. d, The mean odds ratio of a logistic regression of schizophrenia28 is plotted for each LOEUF decile. Error bars in a–d correspond to 95% confidence intervals.