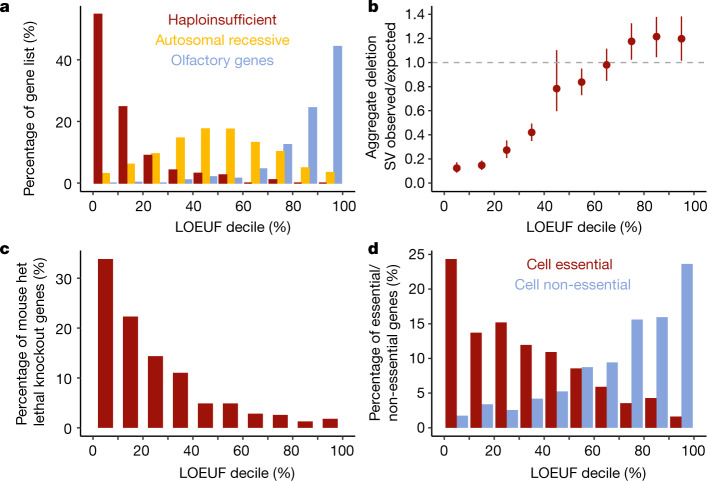
Fig. 3. The functional spectrum of pLoF impact.
a, The percentage of genes in a set of curated gene lists represented in each LOEUF decile. Haploinsufficient genes are enriched among the most constrained genes, whereas recessive genes are spread in the middle of the distribution, and olfactory receptor genes are largely unconstrained. b, The occurrence of 6,735 rare LoF deletion structural variants (SVs) is correlated with LOEUF (computed from SNVs; linear regression r = 0.13; P = 9.8 × 10−68). Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals from bootstrapping. c, d, Constrained genes are more likely to be lethal when heterozygously inactivated in mouse and cause cellular lethality when disrupted in human cells (c), whereas unconstrained genes are more likely to be tolerant of disruption in cellular models (d). For all panels, more constrained genes are shown on the left.