Fig. 5. Disease applications of constraint.
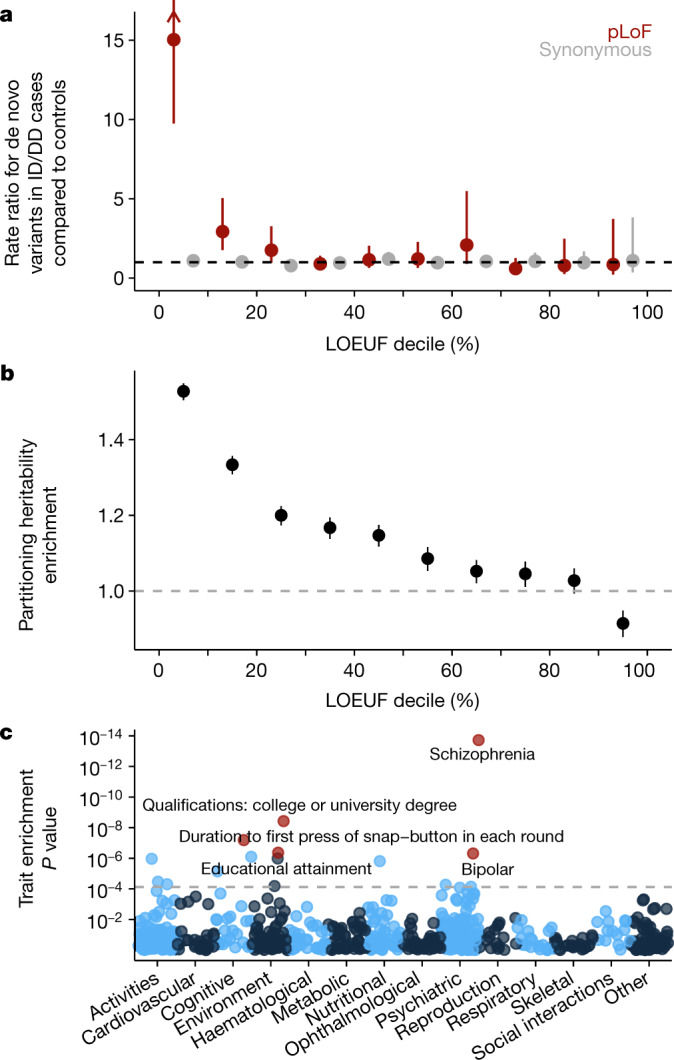
a, The rate ratio is defined by the rate of de novo variants (number per patient) in 5,305 cases of intellectual disability/developmental delay (ID/DD) divided by the rate in 2,179 controls. pLoF variants in the most constrained decile of the genome are approximately 11-fold more likely to be found in cases compared to controls. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. b, Marginal enrichment in per-SNV heritability explained by common (minor allele frequency > 5%) variants within 100-kb of genes in each LOEUF decile, estimated by linkage disequilibrium (LD) score regression48. Enrichment is compared to the average SNV genome-wide. The results reported here are from random effects meta-analysis of 276 independent traits (subsetted from the 658 traits with UK Biobank or large-scale consortium GWAS results). Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. c, Conditional enrichment in per-SNV common variant heritability tested using regression of linkage disequilibrium score in each of 658 common disease and trait GWAS results. P values evaluate whether per-SNV heritability is proportional to the LOEUF of the nearest gene, conditional on 75 existing functional, linkage disequilibrium, and minor-allele-frequency-related genomic annotations. Colours alternate by broad phenotype category.
