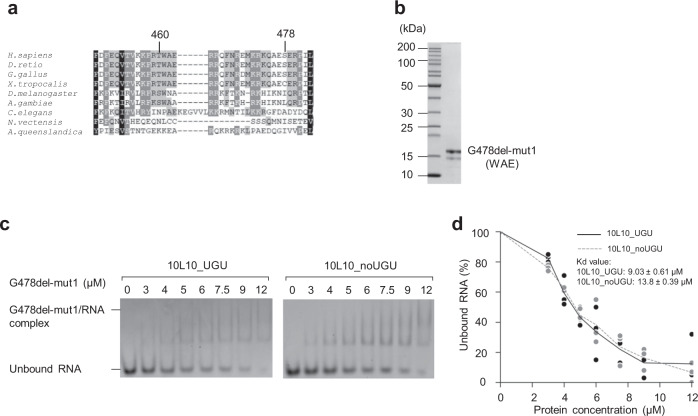
Fig. 3. Amino acids 461–463 are responsible for recognizing the UGU motif.
a Multiple sequence alignment of DGCR8 proteins from different organisms. The alignment method was as previously described17. The region from 448–483 of human (H. sapiens) DGCR8 is shown. Homo sapiens (H. sapiens), Danio rerio (D. rerio), Gallus gallus (G. gallus), Xenopus tropicalis (X. tropicalis), Drosophila melanogaster (D. melanogaster), Anopheles gambiae (A. gambiae), Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans), Nematostella vectensis (N. vectensis), and Amphimedon queenslandica (A. queenslandica). The black, dark gray, and light gray boxes represent 100, 80, and 60% sequence similarities, respectively. b The purified G478del-mut1 protein, which contains amino acids AGQ in the 461–463 region (instead of WAE, which are in the WT protein), was analyzed by SDS-PAGE. c The EMSAs for G478del-mut1. Various amounts of G478del-mut1 (ranging from 0 to 12 μM) were mixed with 1 μM 10L10_UGU or 10L10_noUGU RNA in a 10 μL reaction solution. d Quantification of the EMSA data for G478del-mut1 in (c). The density of each RNA band on the gel was measured using Image Lab 6.0 (Bio-Rad), and the results were obtained from three independent experiments.