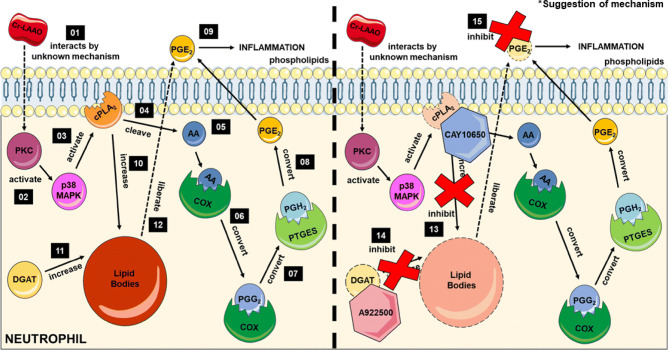
Figure 6.
Suggestion of mechanism of activation of the cyclooxygenase pathway stimulated by Cr-LAAO. The representative scheme shows Cr-LAAO action on neutrophils. Firstly, Cr-LAAO interacts with the cellular membrane by an unknown mechanism (01), leading to PKC activation (02), which stimulates the p38 MAPK phosphorylation (03), and cPLA2 phosphorylation and activation (04). Activated cPLA2 cleaves membrane phospholipids to form arachidonic acid (AA) (05). AA can be catalyzed by COX-1 or COX-2 (06), forming PGH2, metabolized by PTGES (07) to form PGE2 (08) for release (09). Activation of cPLA2 (10) and DGAT (11) may lead to increased numbers of LBs in neutrophils because LB is rich in arachidonic acid (AA) for PGE2 synthesis. Cr-LAAO can utilize LBs content to release PGE2 (12). Thus, in the presence of cPLA2-α (CAY10650) (13) and DGAT (A922500) (14) inhibitors, there is a decrease in the PGE2 level released (15). This figure was created using images from Servier Medical Art Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://smart.servier.com). Servier Medical Art by Servier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License.