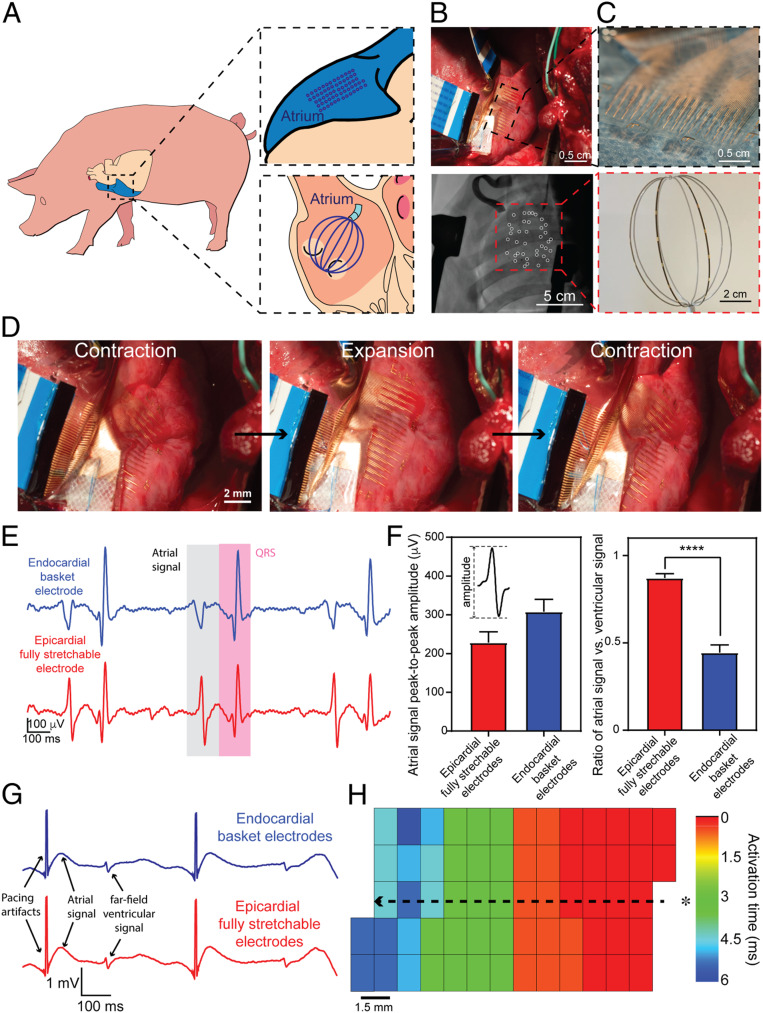
Fig. 4.
Simultaneous in vivo epicardial and endocardial recording on porcine atrium. (A) Schematics showing relative positions of an elastrode array placed on the surface of RA (Right, Upper) and a basket electrode (Right, Lower) placed inside the RA, respectively. (B) Optical photographic image of a representative elastrode array on the surface of the superior RA (Upper) and a fluoroscopic image of a representative basket electrode placed inside the RA (Lower). White circles highlight all of the visible basket electrodes. (C) Photograph of the epicardial elastrode array, with the Inset showing the micrometer-scale electrical sensor (Upper), and optical photographic image of the endocardial basket electrode, with Inset showing the millimeter-scale electrical sensor (Lower). (D) A series of images showing one cycle of the in vivo contraction–expansion for the RA during the electrogram mapping. (E) Representative single voltage tracing from an endocardial basket electrode (blue) and epicardial elastrode (red) from the RA during sinus rhythm. (F) Statistical analysis of the amplitude (Left) and the ratio of the atrial signal to the ventricular signal (Right) from both epicardial and endocardial electrodes. Statistical analysis was performed with unpaired t test (n = 32, P < 0.0001). (G) Representative single voltage trace from the atrial surface paced from a stretchable electrode gives comparable waveform as a standard clinical electrode. (H) Color map shows relative activation-time mapping from the epicardial elastrode array with external pacing, showing that the signal travels away from the external source. This indicates that the stretchable electrode array is capable of capturing atrial signals, and activation maps generated are consistent with what we expect under normal physiological and external electric-signal stimulation conditions. The asterisk (*) indicates the relative location of the external pacing electrode. The dotted line with the arrow indicates the directionality of electric-signal progression from the pacing electrode.