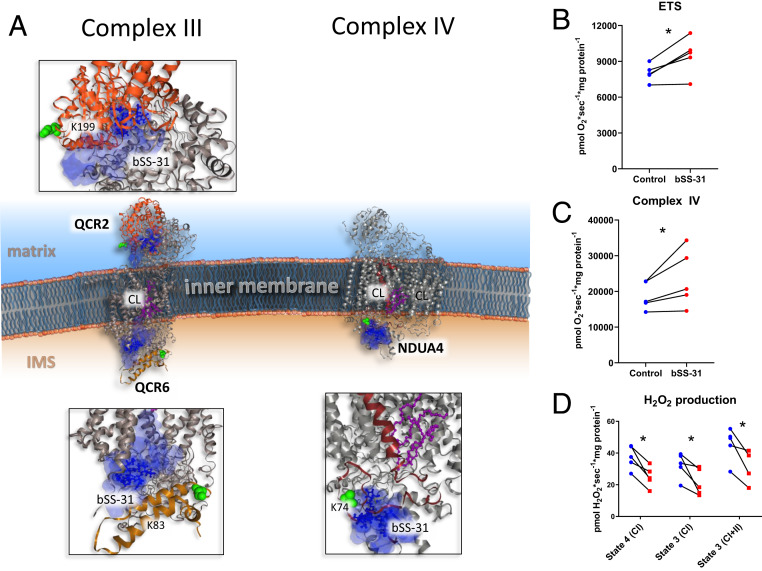
Fig. 3.
Structural and functional impact of bSS-31 interaction with OXPHOS complexes CIII and CIV. (A) Structural view of interaction with subunits QCR2 and QCR6 of CIII and NDUA4 of CIV with Inset showing zoomed view of docked structures. Distance constraints of 0 to 35 Å between the α-carbon of K3 of bSS-31 and the α-carbon of cross-linked lysine were used in molecular docking. Proteins are shown in cartoon view. The top 10 molecular docking results for bSS-31 were included as shown in superimposed semitransparent blue surface view with the top scoring docked position of bSS-31 shown in blue ball-and-stick representation. CL and CL binding residues are shown in magenta ball-and-stick and space-filled representation, respectively. Cross-linked lysines are shown in green spheres. (B) Maximum uncoupled respiration in mitochondria isolated from old mouse hearts in the presence of bSS-31 (red) or vehicle control (blue). See SI Appendix, Fig. S3C for data from young mice. (C) Complex IV activity in the presence of bSS-31 (red) or vehicle control (blue). (D) H2O2 production per O2 consumption in mitochondria isolated in the presence of bSS-31 (red) or vehicle control (blue). *P < 0.05 using a paired t test.