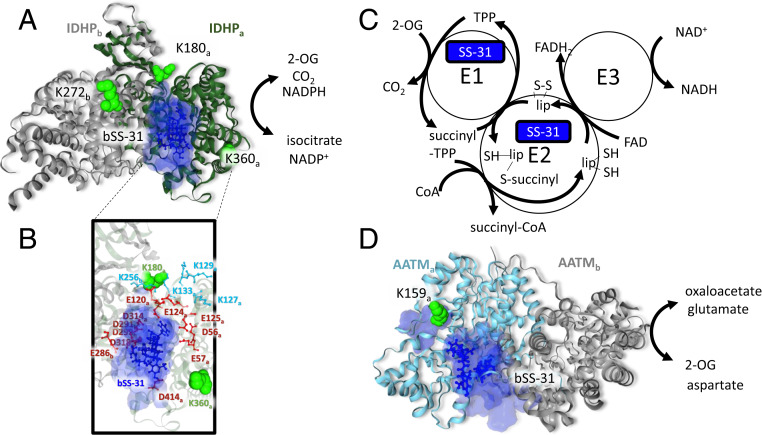
Fig. 6.
SS-31 interaction with 2-oxoglutarate enzymes. (A) bSS-31 interaction with IDHP (PDB: 5h3f) indicated as a homodimer with the IDHPa chain shown as a green ribbon and the IDHPb chain in gray. Lysine residues cross-linked to bSS-31 are displayed as green space-filled residues and labeled with subscript “a” or “b” to indicate which IDHP monomer they are on. bSS-31 (blue ball-and-stick structure) was docked onto the a-subunit using distance restraints for K180 and K360 from the a-subunit and K272 from the b-subunit. The volume encompassing the positions of bSS-31 from the top 10 docking results is displayed as a semitransparent blue surface. (B) View of the bSS-31 interaction interface highlighting surrounding acidic residues (red) and Lys residues (cyan) which are important in maintaining the groove between the large and small domains of IDHP (84). (C) Schematic representation of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex (2-OGDHC). bSS-31 was identified as cross-linked to ODO1 a component of the E1 of 2-OGDHC and ODO2 a component of the E2 portion of 2-OGDHC. (D) bSS-31 interaction with AATM (PDB: 3pdb) shown as a homodimer with the a-chain in teal and the b-chain in gray. Lysine K159 (green space-filled residue) of the a-chain was used to dock bSS-31 into the structure. The volume encompassing the positions of bSS-31 from the top 10 docking results is displayed as a semitransparent blue surface. Interactive versions of the structures can be viewed at xlinkdb.gs.washington.edu/xlinkdb/BiotinylatedSS31_Bruce.php.