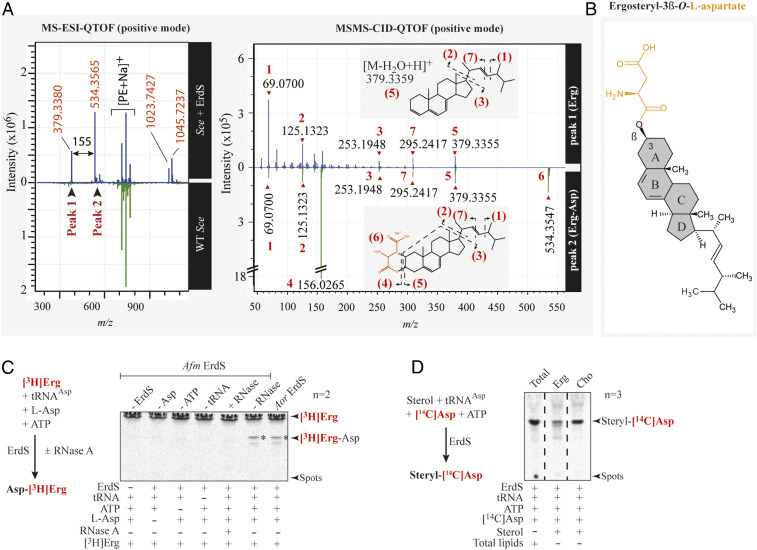
Fig. 4.
Identification of the ergosteryl-3β-O-l-aspartate produced by ErdS in vivo and in vitro. (A) MS-ESI-QTOF spectrum (positive mode) of a lipid fraction containing LX extracted and purified from an Sce WT strain expressing Afm ErdS (upper spectrum, blue) or not (bottom spectrum, green). Peaks 1 and 2 have been analyzed by MS/MS collision-induced dissociation (CID) QTOF analysis in the positive mode. (B) Chemical structure of ergosteryl-3β-O-l-aspartate (Erg-Ap) corresponding to LX deduced from MS spectra shown in A. (C) The [3H]Erg-Asp synthesis was measured by LA assay in the presence of purified Afm ErdS, pure Sce tRNAAsp, radiolabeled [3H]Erg, and cold Asp in the presence (+) or absence (−) of the enzyme or of the indicated substrates. Tests included addition (+) or not (−) of RNase A. [3H]Erg-Asp is indicated with an asterisk. (D) Erg-[14C]Asp synthesis measured by LA assay using purified Afm ErdS, pure Sce tRNAAsp, radiolabeled [14C]Asp, and indicated sterols. LA assay using total lipids from WT Sce was used as a migration control. The adapted LA assay reactions are displayed (simplified) next to the corresponding TLCs. Radiolabeled compounds are highlighted in red, and the number of independent experiments (n) is indicated.