Fig. 5.
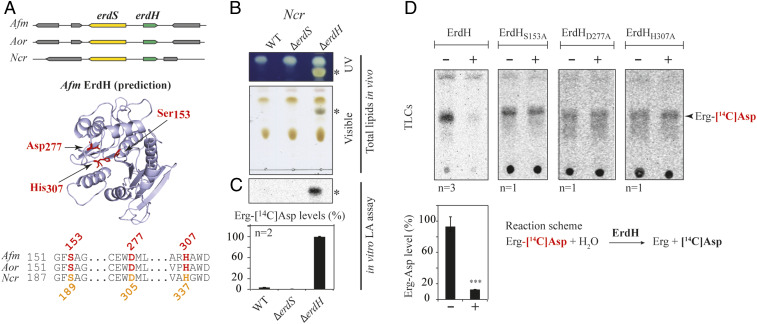
Detection and characterization of ErdH in fungi carrying ErdS. (A) Schematic representation of the genomic context of the erdS (yellow) and erdH (for Erg-Asp hydrolase, in green) genes locus from Afm, Aor, and Ncr that highlights that erdS and erdH are found in a divergent orientation. Phyre2-based α/β-hydrolase−like predicted structure of Afm ErdH and active site alignments of Afm, Aor, and Ncr ErdHs. Ser-Asp-His catalytic triads of α/β-hydrolases/lipases (S153, D277, and H307 in Afm ErdH) are displayed and highlighted on the structure prediction and the alignment. (B) Total lipids from WT, ∆erdS, and ∆erdH Ncr strains were separated by TLC and stained with sulfuric acid/MnCl2 and observed under UV or visible light (n = 3); * indicates Erg-Asp. (C) In vitro measurements of Erg-[14C]Asp synthesis by LA assay using protein extracts from the WT, ∆erdS, and ∆erdH Ncr strain protein extracts, using pure Sce tRNAAsp as a substrate (n = 2). (D) In vitro measurement of the Erg-[14C]Asp hydrolase activities of purified recombinant WT (n = 3) or catalytic mutant Ncr ErdHs (n = 1). (C and D) The Student's t test was used to determine significance of the means of the data; ***P < 0.005.