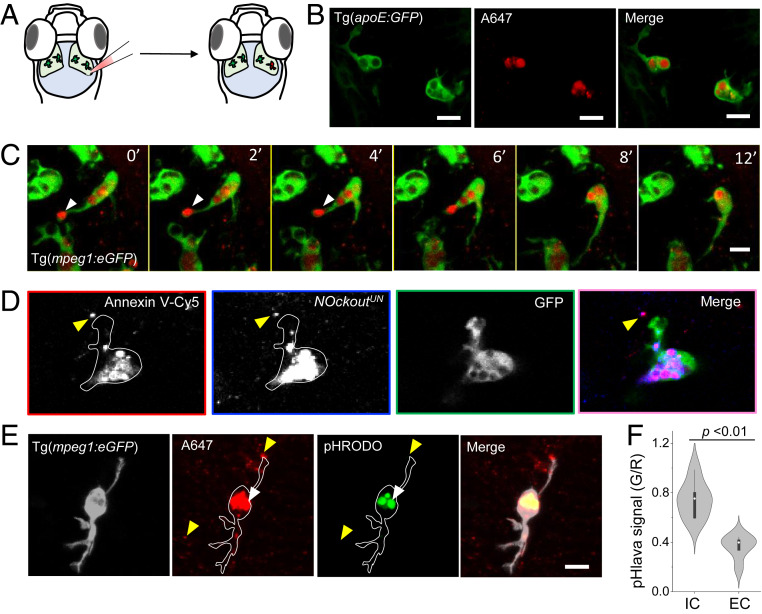
Fig. 3.
NOckoutUN localizes in phagosomes of zebrafish microglia in vivo. (A) Schematic of the larval transgenic zebrafish brain expressing GFP in microglia (Tg(apoE:GFP)). NOckoutUN (0.2 pmol in HBSS) was microinjected in the optic tectum of 3-dpf-old fish. (B) Images acquired 1 h postinjection of NOckoutUN (0.2 pmol in HBSS) shows probe localization in phagosomes of microglia in Tg(apoE:GFP) fish. (C) Time-lapse images (0 min to 12 min) shows NOckoutUN uptake by microglia. Fusion of newly formed phagosomes with existing phagosomes is also observed (white arrowhead). (D) Colocalization of NOckoutUN with apoptotic body marker annexin V−Cy5 prior to phagocytosis by microglia (yellow arrowhead). (E) Representative images of pHlava injected in Tg(mpeg1:eGFP) fish shows strong signal in phagosomes (white arrowhead) in the pHrodo channel (λem = 570 nm), while extracellular puncta show no signal (yellow arrowhead), indicating high and low acidities, respectively. (F) The pHlava signal from the phagosomes (IC) and the extracellular milieu (EC) are plotted as the ratio of pHrodo to A647 channel intensities (n = 16 phagosomes from n = 8 fish). All experiments were performed in triplicate. (Scale bar, 10 μm.) P values are obtained using Kruskal−Wallis statistical test.