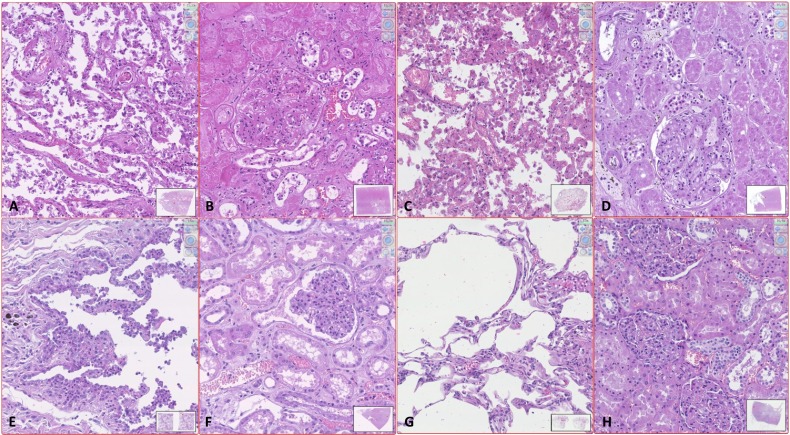
Fig. 2.
Standard quality of histology in early performed autopsy (EPA) versus late autopsy (LA) or surgical samples (SS).
A–D. Autopsy performed more than 24 h after death: examples of histological samples of patients SARS-CoV-2 positive (A and B) and patients SARS-CoV-2 negative (C and D). In both cases the lungs (A and C) have numerous pneumocytes inside the alveolar cavities and the alveolar septa are widely disepithelized; without immunohistochemical staining it is difficult to distinguish intraalveolar pneumocytes from macrophages and to differentiate type 1 from type 2 pneumocytes. The renal parenchyma (B and D) also shows an unsatisfactory morphological detail that makes it difficult to distinguish the damage consequent to the present pathologies from postmortem degeneration. The glomeruli are collapsed and difficult to read. The proximal tubules present loss of the nuclear basophilia and swollen cytoplasm with ill-defined limits; the distal tubules show widespread intraluminal disepithelization of the epithelium. E–F. Autopsy performed 2 h after death on patients SARS-CoV-2 positive. The pulmonary picture (E) appears markedly different from image A: the pneumocytes are widely adherent to the alveolar wall and swollen, in particular those of type 2; the capillaries in the septa are often dilated and the intraluminal erythrocytes are well preserved. The histological quality is comparable to that of the lung SS in image G. The morphological quality of the renal sample of EPA is also comparable to that of the renal SS (H), while it differs significantly from the quality of sample D from LA. In image F the tubular epithelia are not detached from the wall and the nuclei are well recognizable, the blood cells are well conserved and the glomerulus is not collapsed. G–H. SS of lung (G) and kidney (H). (Digital histological slide; Nanozoomer S360, Hamamatsu; in the box at the bottom right of each image it is indicated the area of the sample highlighted in the image; the magnification of the image is indicated in the upper right corner.)