Figure 6.
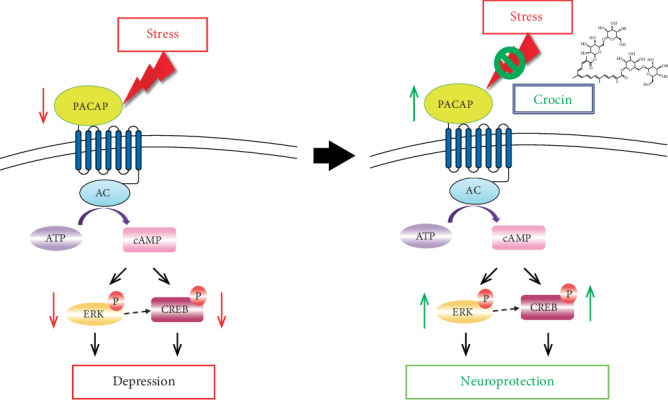
A schematic illustration of the proposed mechanism for the neuroprotective effect of crocin in depression. Stress inhibits the expression of PACAP, thereby inhibiting the phosphorylation of its downstream ERK and CREB, and then reduces the translation of synaptic plasticity proteins, finally leading to depressed-like behaviors. Crocin can activate ERK and CREB signaling pathways via upregulating endogenous PACAP, then enhance synaptic plasticity and improve neuron survival, and play an antidepressant role in mice CUMS model and corticosterone cell model.
