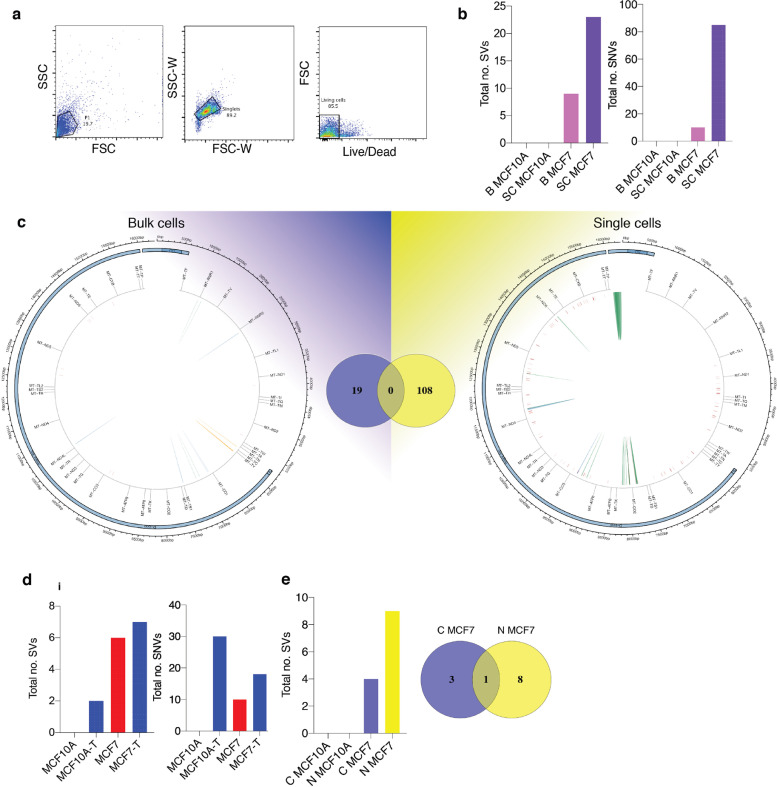
Fig. 4.
Validation of MitoSV-seq in breast cancer cell lines. (a) Single-cell isolation from MCF10A and MCF7 cell lines. Cell were stained with LIVE/DEAD Fixable Violet, and single living cells were sorted. (b) Evaluation of MitoSV-seq in bulk vs single cells.
Biological samples were used in triplicate. B: bulk; SC: single cell. (c) Schematic of distribution of human mtDNA detected in bulk and single cells by MitoSV-seq. Total numbers of detected variations in each condition and their overlapping variations are depicted in the Venn diagrams in the middle. Circos plots of human mtDNA genome displaying heavy and light origins of replication (OH and LO, respectively), major arc, and D-loop (outer blue circle). mtDNA genes are displayed in the middle circle (grey lines). Shown are SVs as arches with deletions (blue), tandem duplications (red), inversions (green), and insertions (orange). Thickness of the arches corresponds to SV heteroplasmy. SNVs are marked with short red lines (_) according to their positions in mouse mtDNA. Intensity of red lines corresponds to SNV heteroplasmy. (d) Mild oxidative stress with H2O2 in MCF10A and MCF7 cell lines introduces SVs and SNVs in mtDNA. T: treated. (e) Comparison of conventional technique with MitoSV-seq to identify SVs in bulk sample. C, conventional technique; N, new (MitoSV-seq).