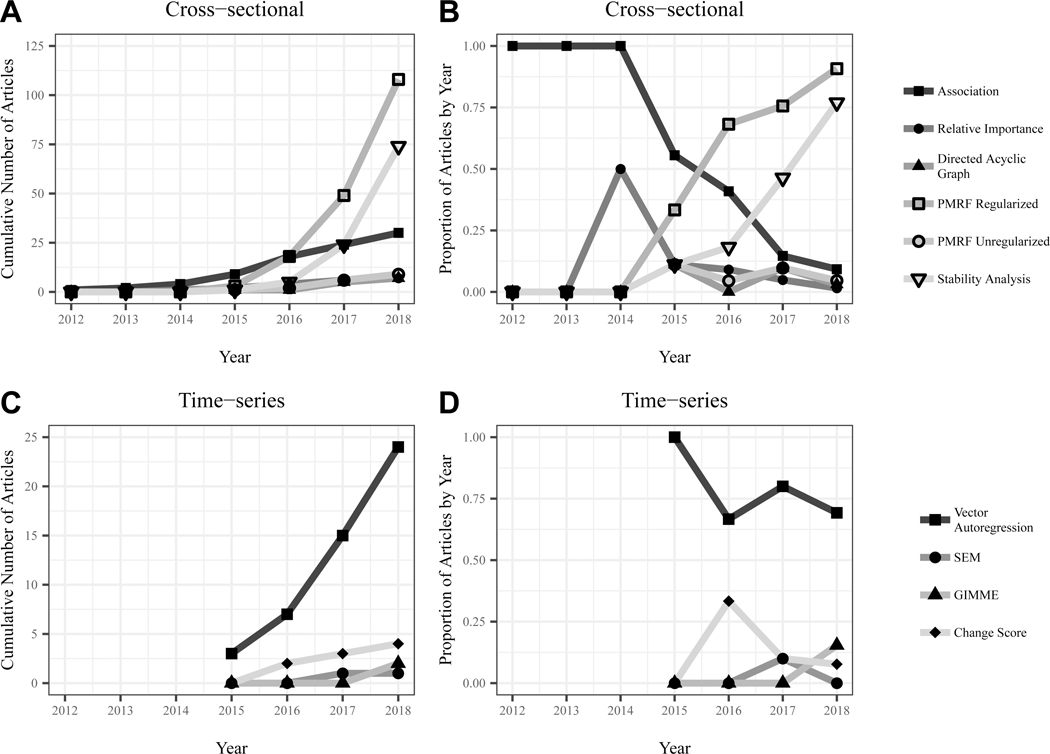
Figure 4. Network estimation methods commonly utilized in empirical network studies.
This figure depicts methods commonly used in estimating network structure from cross-sectional (panels A & B) and time-series data (panels C & D). Panels A & C depict the cumulative number of articles applying a given estimation method for cross-sectional and time-series data, respectively. Panels B & D depict the proportion of articles in a given year that utilized these estimation methods. For the purposes of this summary, we considered any network based on multiple time points to be based on “time-series” data, thus incorporating change score networks into this category. Note that the earliest cross-sectional (Cramer et al., 2010a) and time-series (Bringmann et al., 2013) networks were regarded as theoretical and methodological contributions, respectively, given their substantial contributions in these domains, and thus are not included in this report. PMRF = Pairwise Markov Random Field; SEM = Structural Equation Modeling; GIMME = Group Iterative Multiple Model Estimation