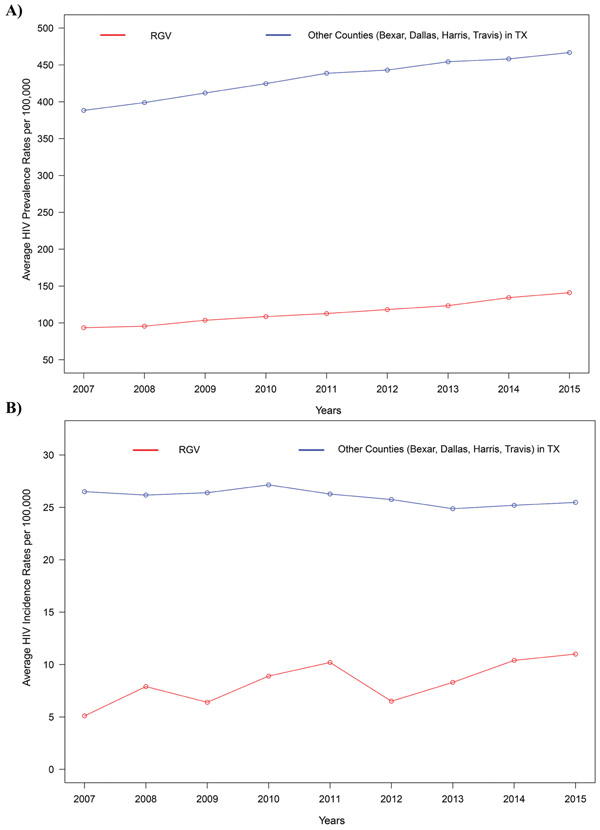
Fig. (2).
(A) A trend analysis using the Mann-Kendall test was performed in order to investigate the change in the average HIV-1 prevalence rates per 100,000 in the RGV compared to four other highly populated counties in Texas namely Bexar, Dallas, Harris, and Travis during the period from 2007 to 2015. Both, average HIV-1 prevalence rates in the RGV and Other areas of Texas depict significantly increasing trends (p-value=0.0003) at a 5% level of significance. (B). A trend analysis using the Mann-Kendall test was performed in order to investigate the change in the average HIV-1 incidence rates per 100,000 in the RGV compared to four other highly populated counties in Texas namely Bexar, Dallas, Harris, and Travis during the period from 2007 to 2015. Average HIV-1 incidence rates in the RGV depicted a significantly increasing trend (p-value=0.0165) whereas other areas of Texas resulted in a significantly decreasing trend (p-value=0.0476) at a 5% level of significance. Data for this analysis was obtained from the Texas Department of State Health Services (https://www.dshs.texas.gov/records) and Texas State Library and Archives Commission (https://www.tsl.texas.gov/ref/abouttx/popcnty2010-11.html).