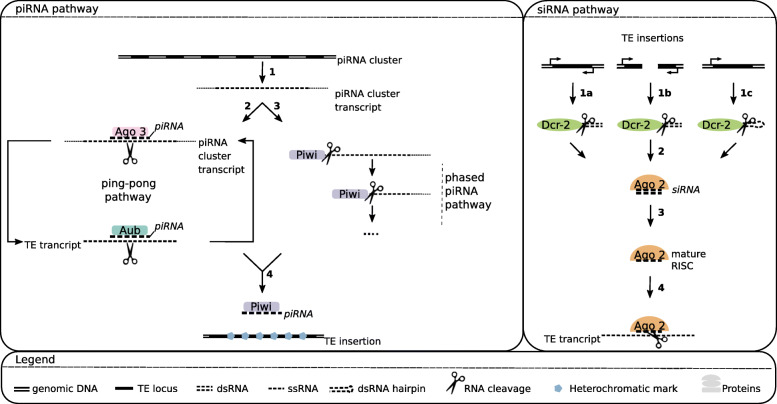
Fig. 4.
small RNA pathways controlling TEs. piRNA pathway: 1. RNA PolII transcribes a genomic piRNA cluster into a long single stranded RNA. 2. The transcript thus formed enters the ping-pong pathway, which is ensured by Aub and Ago3, generates sense and antisense piRNAs, and ensure post-transcriptional silencing by transcript slicing. 3. Piwi directs the cleavage of the piRNA cluster transcript and generates a piRNA. This step may be repeated. 4. Transcriptional silencing: in the nucleus, a piRNA guides Piwi and promotes H3K9 methylation of TE DNA sequences. siRNA pathway: 1. Generation of a long dsRNA by: a. bi-directional transcription of a unique TE locus, b. interaction of two complementary transcripts from distinct TE loci. c. hairpin formation, due for example to inverted repeats binding 2. Dcr-2 processes long dsRNAs into siRNAs, which are loaded on Ago2. 3. The passenger strand of the siRNA is sliced by Ago2, only the guide strand remains. 4. The RISC binds to a TE transcript with sequence complementarity to the guide strand and Ago2 cleaves it.