Figure 4. H3K36me1/2 and H3K36me3 Have Unique Phenotypes in Some Cellular Contexts.
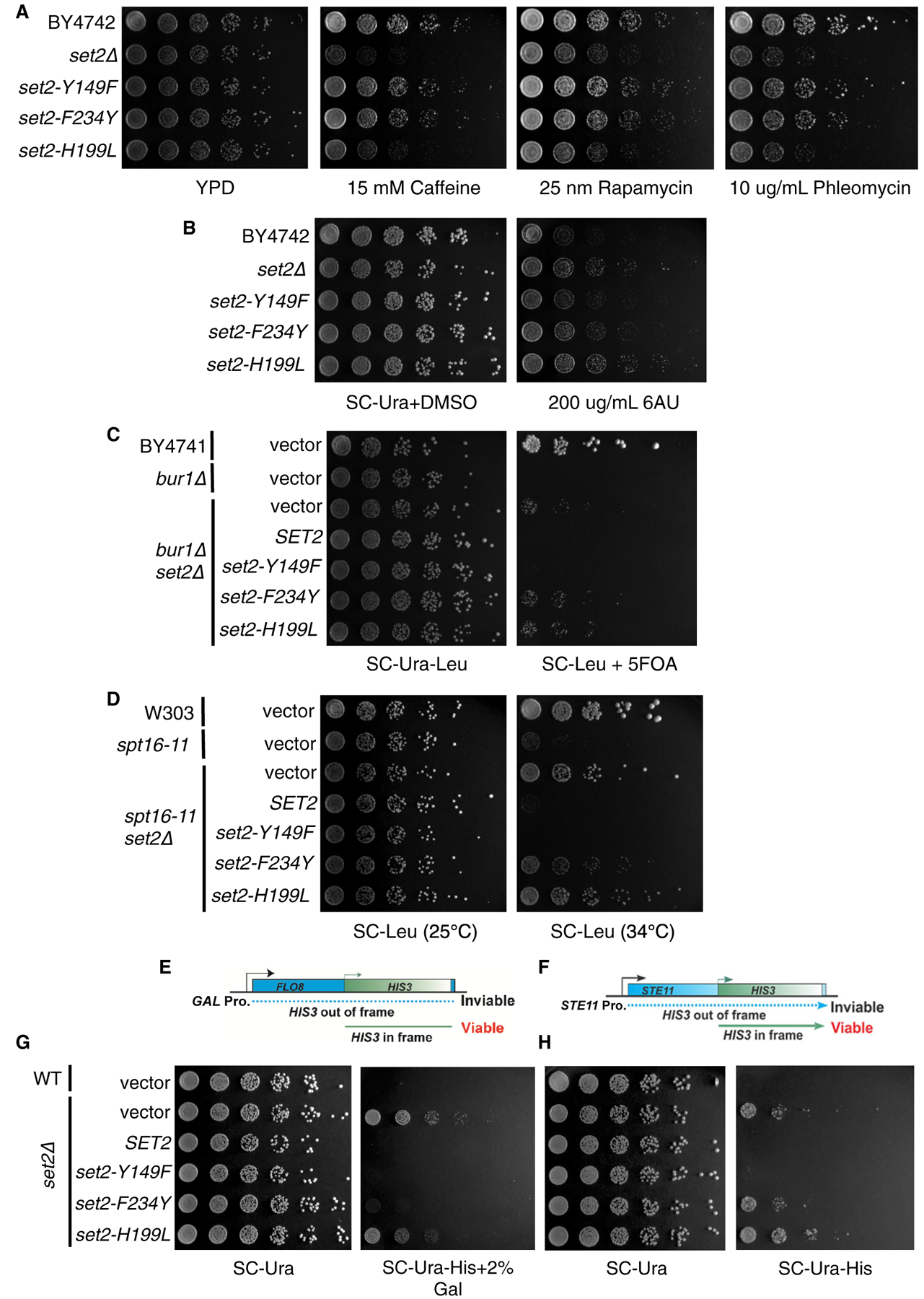
(A) Five-fold serial dilutions of BY4742, set2Δ, and set2 mutant strains plated on YPD or YPD containing caffeine (15 mM), rapamycin (25 nM), or phleomycin (10 μg/mL). (B) Five-fold serial dilutions of BY4742, set2Δ, and set2 mutant strains plated on SC-Ura containing DMSO or 200 μg/mL 6-AU. (C) Five-fold serial dilutions of BY4741, bur1Δ, and set2 mutant strains plated on SC-Ura-Leu or SC-Ura-Leu containing 5-fluoorotic (5-FOA). (D) Five-fold serial dilutions of W303, spt16–11, and set2 mutant strains plated on SC-Leu and incubated at 25°C or 34°C. (E) Schematic of FLO8-HIS3 fusion gene reporter to detect cryptic transcription. (F) Schematic of STE11-HIS3 fusion gene reporter to detect cryptic transcription. (G) Five-fold serial dilutions of indicated WT, set2Δ, and set2 mutant strains plated on SC-Ura, SC-Ura-His with 2% galactose, or SC-Ura-His. All spotting assays were repeated three times, and the images shown are representative of the data.
