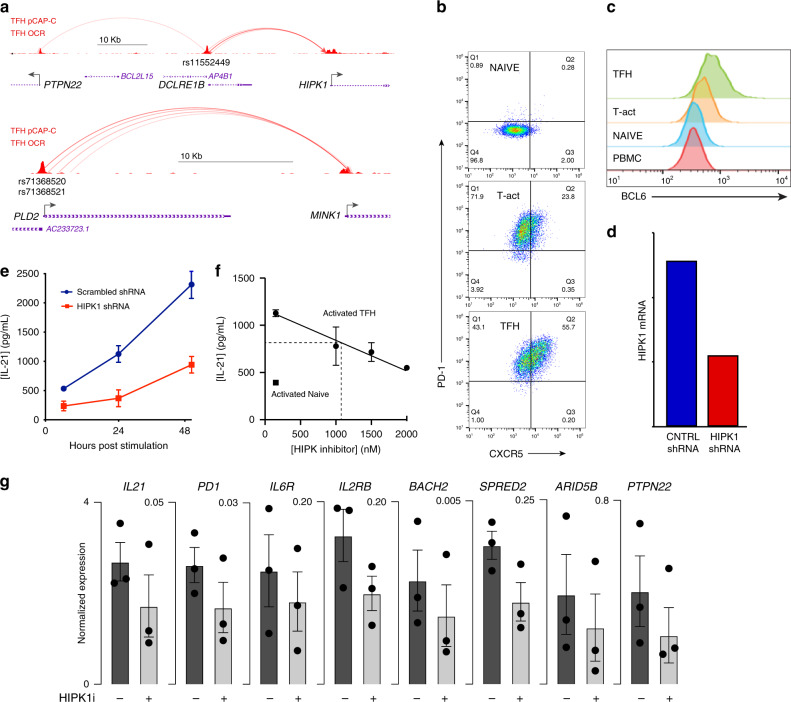
Fig. 9. SLE variant-to-gene mapping implicates drug targets for modulation of TFH function.
a The interactomes of SLE proxies rs11552449 (r2 = 0.97), rs71368520 (r2 = 0.5), and rs71368521 (r2 = 0.5) implicate HIPK1 and MINK1. b Purified naive CD4+ T cells cultured under neutral (Tact) or TFH-skewing (TFH) conditions show increased expression of PD-1 and CXCR5, as well as BCL-6 (c). d HIPK1 mRNA expression by in vitro-differentiated TFH cells transduced with scrambled Lenti-shRNA or Lenti-HIPK-1 shRNA. e shRNA-mediated knock-down of HIPK1 inhibits IL-21 secretion by TFH cells. A HIPK inhibitory drug causes dose-dependent inhibition of IL-21 production (f) and expression of several SLE-associated gene (g) by TFH cells. All data in e and f are mean ± SEM and are representative of three independent experiments. Data in g depict the mean (columns) ± SEM (error bars) normalized gene expression by three individual donor T cell cultures (circles). Statistical significance of the effect of HIPK inhibition was determined by t-test (two-tailed). P values are: BACH2, 0.01; SPRED2, 0.02; IL2RB, 0.03; ARID5B, 0.03; PD1, 0.04; IL6R, 0.04; PTPN22, 0.05; IL21, 0.06. Source data are provided as a Source data file.