Fig. 2. The mechanism of Rad51-dependent subtelomere recombination.
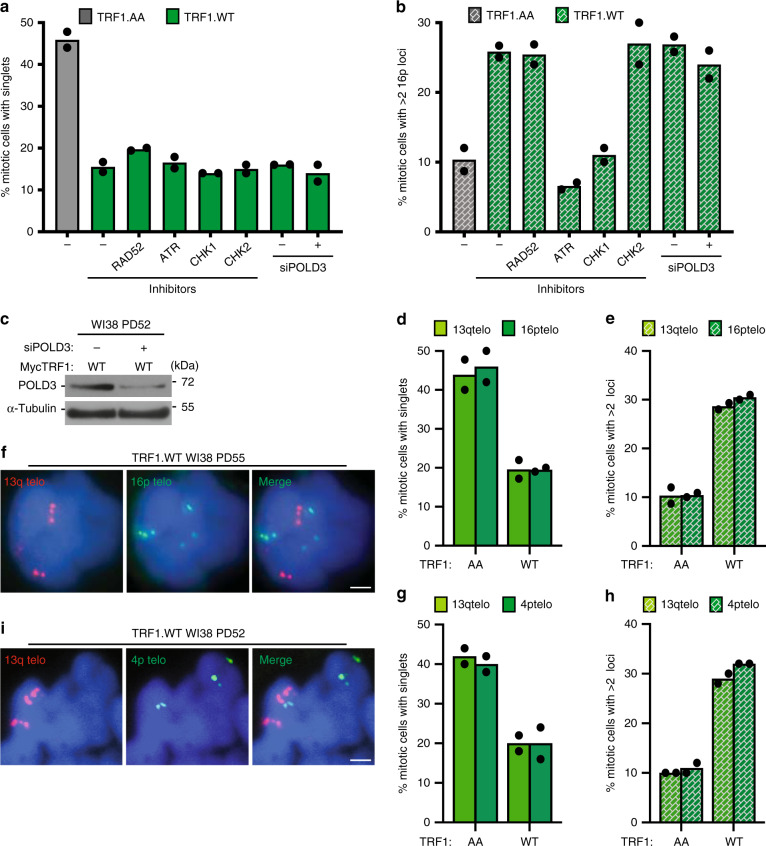
Quantification of the frequency of TRF1.AA or TRF1.WT transfected late (PD50-53) WI38 mitotic cells (a) with cohered telomeres or (b) exhibiting subtelomere copying measured by FISH analysis with a 16p telo probe following treatment with the indicated inhibitors or siRNA. Average of two independent experiments (n ≥ 25 cells each). c Immunoblot analysis of TRF1.WT-transfected, POLD3 siRNA-treated late (PD52) WI38 cell extracts. d, e Quantification of the frequency of WI38 TRF1.AA or TRF1.WT transfected late (PD52-55) mitotic cells (d) with cohered telomeres or (e) exhibiting subtelomere copying measured by dual FISH analysis with 13q and 16p telo probes. Average of two independent experiments (n ≥ 46 cells each). f FISH analysis of a WI38 TRF1.WT transfected late (PD55) mitotic cell exhibiting subtelomere copying using 13q (red) and 16p (green) telo probes. g, h Quantification of the frequency of TRF1.AA or TRF1.WT transfected late (PD52) WI38 mitotic cells (g) with cohered telomeres or (h) exhibiting subtelomere copying measured by dual FISH analysis with 13q and 4p telo probes. Average of two independent experiments (n = 50 cells each). i FISH analysis of a TRF1.WT transfected late (PD52) WI38 mitotic cell exhibiting subtelomere copying using 13q (red) and 4p (green) telo probes. f, i DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars represent 2 μm. Experiments were repeated independently twice (for c, f, i) with similar results. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.